Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2017; 23(13): 2318-2329
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318
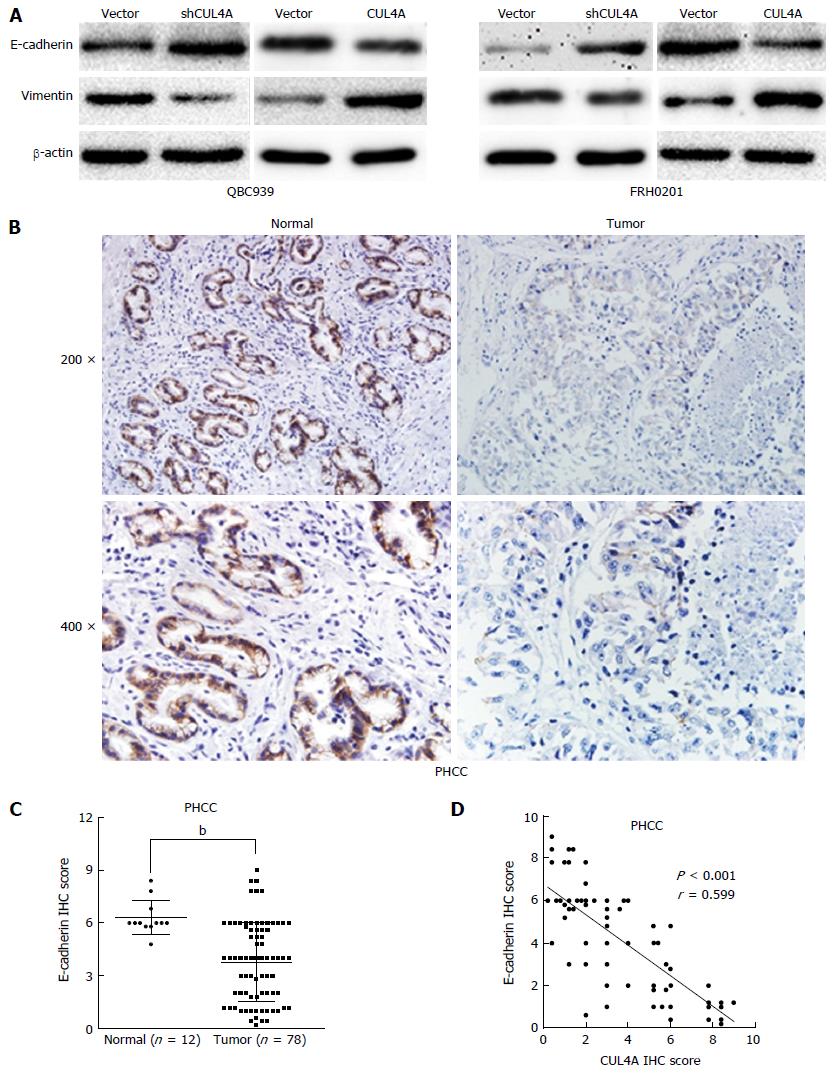
Figure 4 Cullin 4A induces the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Expression levels of an epithelial marker (E-cadherin) and mesenchymal marker (vimentin) were analyzed by Western blot; B: Representative IHC images of E-cadherin expression in PHCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues; C: Statistical analysis of the semiquantification of E-cadherin expression in PHCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues; D: Linear regression analyses of IHC scores between CUL4A and E-cadherin expression in PHCC. bP < 0.01 based on the Student’s t-test. CUL4A: Cullin 4A; PHCC: Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma.
- Citation: Zhang TJ, Xue D, Zhang CD, Zhang ZD, Liu QR, Wang JQ. Cullin 4A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(13): 2318-2329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i13/2318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318