Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2017; 23(13): 2318-2329
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318
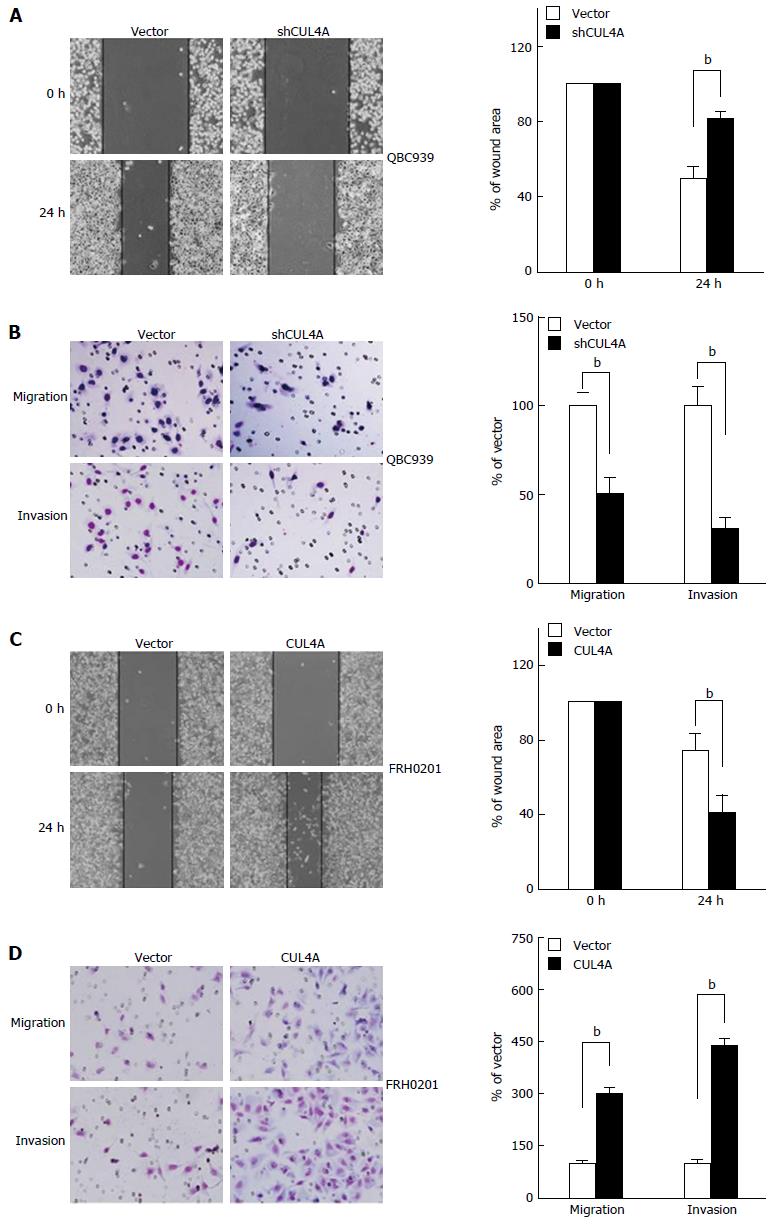
Figure 3 Cullin 4A promotes the migration and invasion of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
QBC939-shCUL4A and FRH0201-CUL4A cells or control cells were subjected to wound healing (A and C), Transwell migration (B and D, top), and Matrigel invasion (B and D, bottom) assays. A: Quantification was performed by measuring the uncovered areas compared with the controls; B: Quantification of migrated cells through the membrane and invaded cells through the Matrigel of each cell line is shown as proportions to their controls; C: Quantification was carried out by measuring the uncovered areas compared with the controls; D: Quantification of migrated cells through the membrane and invaded cells through Matrigel for each cell line is shown as proportions to their controls. bP < 0.01 based on the Student’s t-test. All results are from at least three independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SD. CUL4A: Cullin 4A.
- Citation: Zhang TJ, Xue D, Zhang CD, Zhang ZD, Liu QR, Wang JQ. Cullin 4A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(13): 2318-2329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i13/2318.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2318