Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2017; 23(13): 2294-2307
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2294
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2294
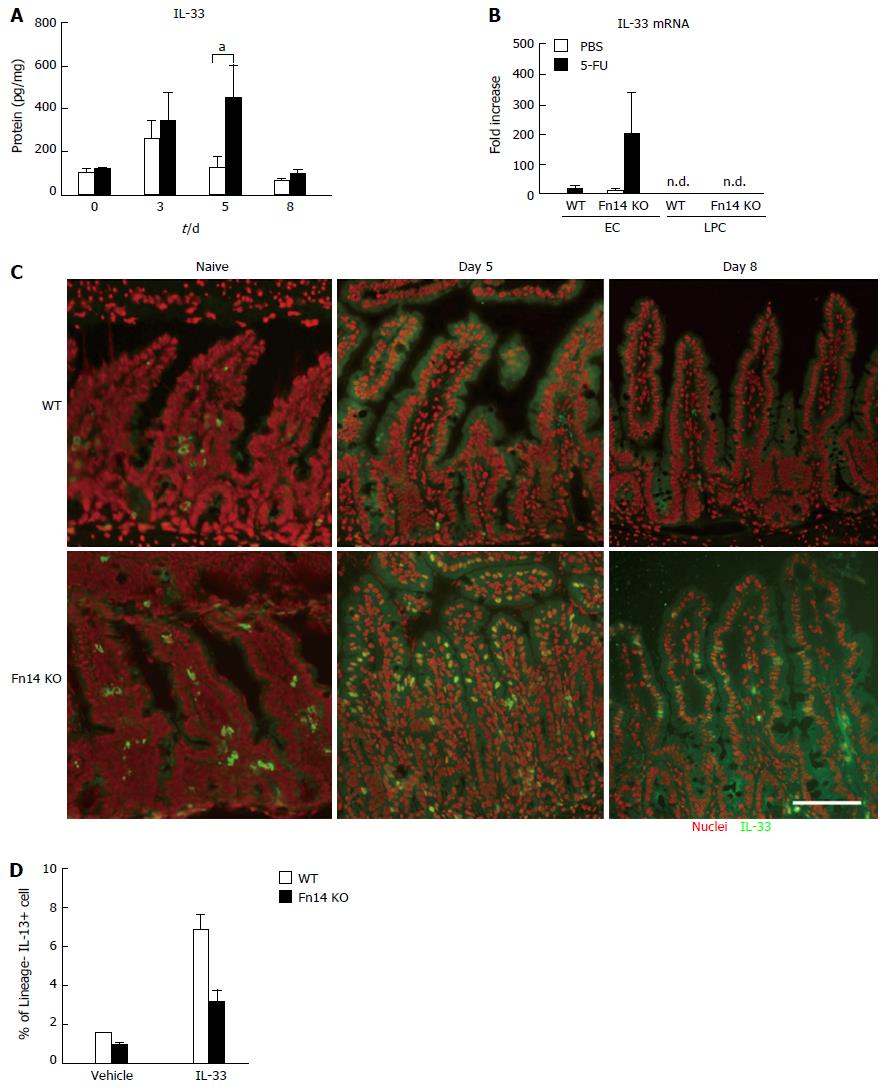
Figure 5 IL-33-induced IL-13 expression was Fn14 dependent.
A: IL-33 levels were measured from homogenate of the ileum after injection of 5-FU (n = 4 mice per time point). Open bar, WT mice; solid bar, Fn14 KO mice (n = 4 mice per time point). Data are shown as mean ± SD (aP < 0.05); B: Fold increase of IL-33 mRNA in ECs and LPCs on day 5 after injection of 5-FU (n = 3 mice per experiment). Data are shown as mean ± SD; C: Sections were prepared from samples collected on days 0 (naïve), 5, and 8 after injection of 5-FU from WT and Fn14 KO mice and probed with anti-IL-33 antibody (green) (n = 3 mice per experimental condition). Red: Nuclear staining. Scale bar = 100 µm. Representative images are provided; D: LPCs from naïve WT or Fn14 KO ileum were stimulated with recombinant IL-33 in vitro and the number of IL-13-producing cells per mouse was measured using flow cytometry. Results of repeated experiments (n = 3) are summarized.
- Citation: Sezaki T, Hirata Y, Hagiwara T, Kawamura YI, Okamura T, Takanashi R, Nakano K, Tamura-Nakano M, Burkly LC, Dohi T. Disruption of the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway prevents 5-fluorouracil-induced diarrhea in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(13): 2294-2307
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i13/2294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2294