Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2017; 23(13): 2276-2285
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2276
Published online Apr 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2276
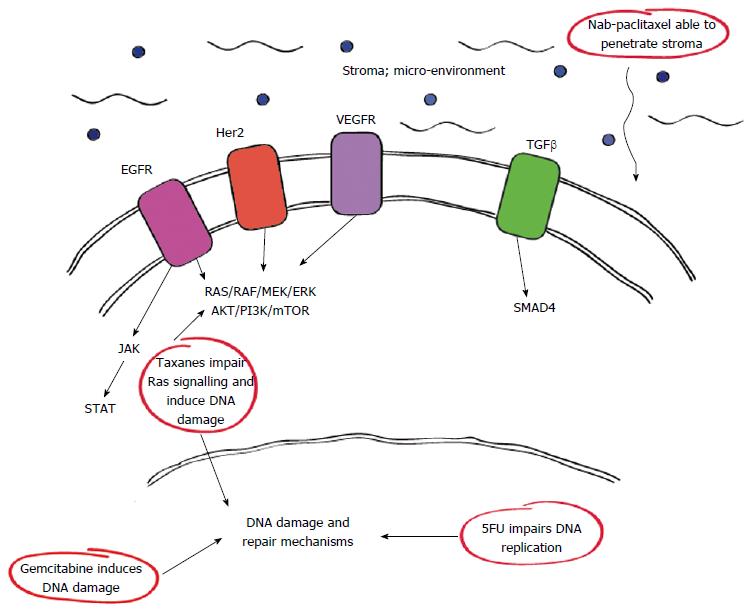
Figure 1 Schematic of major pathways associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and site of action of current treatments.
Multiple pathways and receptors are associated with the development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) including epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2), and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR). All of these have important roles in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and AKT/PI3K/mTOR pathways involved in cell growth. EGFR also has a role in the JAK/STAT pathway necessary for activation of signalling cascades and gene transcription. Transforming growth factor (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine involved in various processes some of which are mediated by SMAD 4, a known mutation associated with development of PDAC. Current therapeutics target these processes at various sites.
- Citation: Diwakarla C, Hannan K, Hein N, Yip D. Advanced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma - Complexities of treatment and emerging therapeutic options. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(13): 2276-2285
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i13/2276.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i13.2276