Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2017; 23(12): 2149-2158
Published online Mar 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2149
Published online Mar 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2149
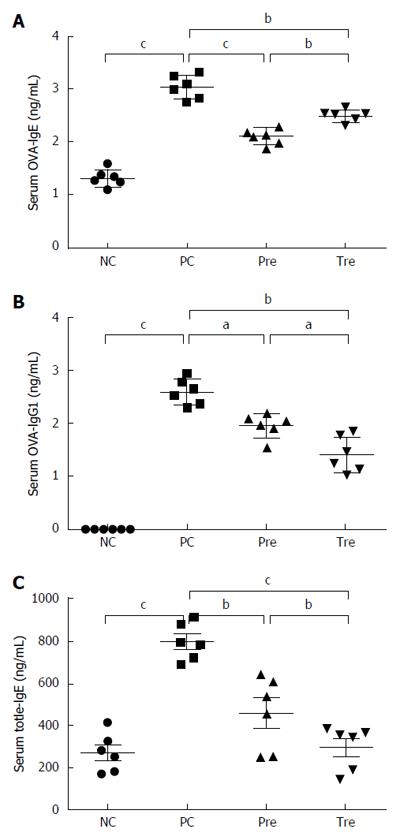
Figure 3 Effect of B.
infantis CGMCC313-2 on the reversal of IgE and IgG1 in ovalbumin-induced asthma and β-lactoglobulin-induced food allergy mouse models. A and B: There were significant increases in OVA-specific IgE and IgG1 expression in the positive control (PC; Group 2) group compared with the normal control (NC; Group 1) group in the allergic asthma mouse model. The prevention (pre; Group 3) and pre-treatment (tre; Group 4) groups following B. infantis CGMCC313-2 administration showed decreased expression; C: A significant increase in total IgE expression was seen in the positive control (PC; Group 2) group compared with the normal control (NC; Group 1) group in the BLG-induced food allergy mouse model. The prevention (pre; Group 3) and pre-treatment (tre; Group 4) groups following B. infantis CGMCC313-2 administration showed decreased expression. The statistical differences are represented as follows: aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01, and cP < 0.001.
- Citation: Liu MY, Yang ZY, Dai WK, Huang JQ, Li YH, Zhang J, Qiu CZ, Wei C, Zhou Q, Sun X, Feng X, Li DF, Wang HP, Zheng YJ. Protective effect of Bifidobacterium infantis CGMCC313-2 on ovalbumin-induced airway asthma and β-lactoglobulin-induced intestinal food allergy mouse models. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(12): 2149-2158
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i12/2149.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2149