Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2017; 23(11): 1980-1989
Published online Mar 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.1980
Published online Mar 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.1980
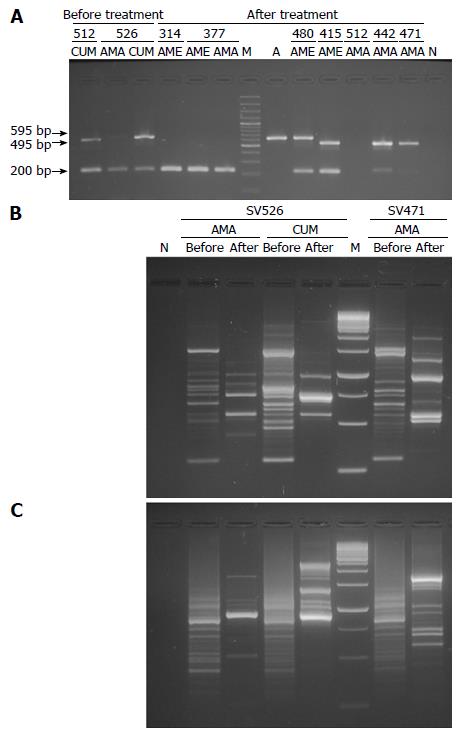
Figure 1 Electrophorectic analyses.
A: EPIYA-PCR products from DNA of H. pylori isolates obtained before (first endoscopy) and after (second endoscopy) treatment in patients with treatment failure, the PCR products were analyzed in agarose gel at 2%. Line A positive control, clinical isolate of H. pylori (PZ5085) with EPIYA motif ABCC (570 ± 25 bp) confirmed through sequencing; line M, 100-bp weight marker; line N, negative reaction control. The distribution of the different molecular weights among isolates is an indication of the presence of multiple EPIYA repetitions; B and C: RAPD patterns generated with primer 1281 and 1254, respectively, in H. pylori isolates obtained before and after anti-H. pylori treatment; line N: Negative reaction control; line M: 100-bp weight marker. ALC: Antrum lesser curvature; AGC: Antrum greater curvature; BGC: Body greater curvature; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
- Citation: Bustamante-Rengifo JA, Matta AJ, Pazos AJ, Bravo LE. Effect of treatment failure on the CagA EPIYA motif in Helicobacter pylori strains from Colombian subjects. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(11): 1980-1989
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i11/1980.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.1980