Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2017; 23(10): 1816-1827
Published online Mar 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1816
Published online Mar 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1816
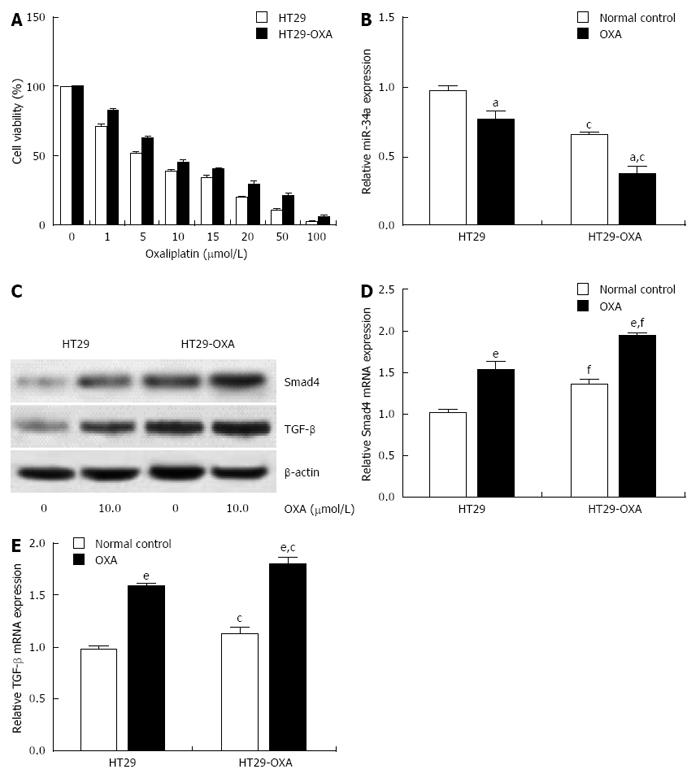
Figure 2 Oxaliplatin treatment inhibited miR-34a expression and activated the TGF-β/Smad4 pathway.
A: HT29 and HT29-oxaliplatin (OXA) cells were incubated with serial concentrations of OXA for 48 h and cell viability (%) was measured by CCK-8 kit and normalized with the corresponding untreated cells; B: HT29 and HT29-OXA cells were incubated with OXA (10 μmol/L) for 48 h and expression of miR-34a was determined by qRT-PCR. U6 was used as an internal control; C: The above cells lysates were examined with indicated antibodies by western blotting. β-actin was used as loading control; D and E: The above cells were subjected to qRT-PCR to measure Smad4 and TGF-β mRNA expression levels. β-actin was used as the internal control (aP < 0.05, eP < 0.001 indicates a significant difference vs normal control. cP < 0.05, fP < 0.001 indicates a significant difference vs respective untreated cells).
- Citation: Sun C, Wang FJ, Zhang HG, Xu XZ, Jia RC, Yao L, Qiao PF. miR-34a mediates oxaliplatin resistance of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting macroautophagy via transforming growth factor-β/Smad4 pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(10): 1816-1827
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i10/1816.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1816