Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2017; 23(10): 1735-1746
Published online Mar 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1735
Published online Mar 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1735
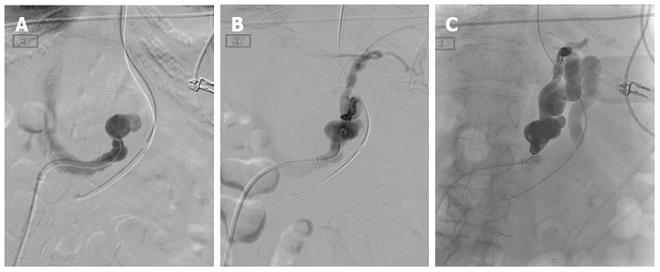
Figure 16 Coil-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration of gastric varices in a 55-year-old patient who presented with recurrent gastric variceal bleeding refractory to endoscopic therapy.
A: Angled catheter was navigated into the left gastrorenal shunt after obtaining access from the right common femoral vein and advancing 5-french sheath into the inferior vena cava; B: Digital subtraction angiography performed through the gastrorenal shunt demonstrating large dilated shunt vessels, as well as, secondary outflow through pericardiophrenic collaterals; C: Both the proximal and distal shunts were coil-occluded and gelfoam was utilized to embolize and thrombose the gastric varices.
- Citation: Bandali MF, Mirakhur A, Lee EW, Ferris MC, Sadler DJ, Gray RR, Wong JK. Portal hypertension: Imaging of portosystemic collateral pathways and associated image-guided therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(10): 1735-1746
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i10/1735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1735