Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2017; 23(1): 76-86
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.76
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.76
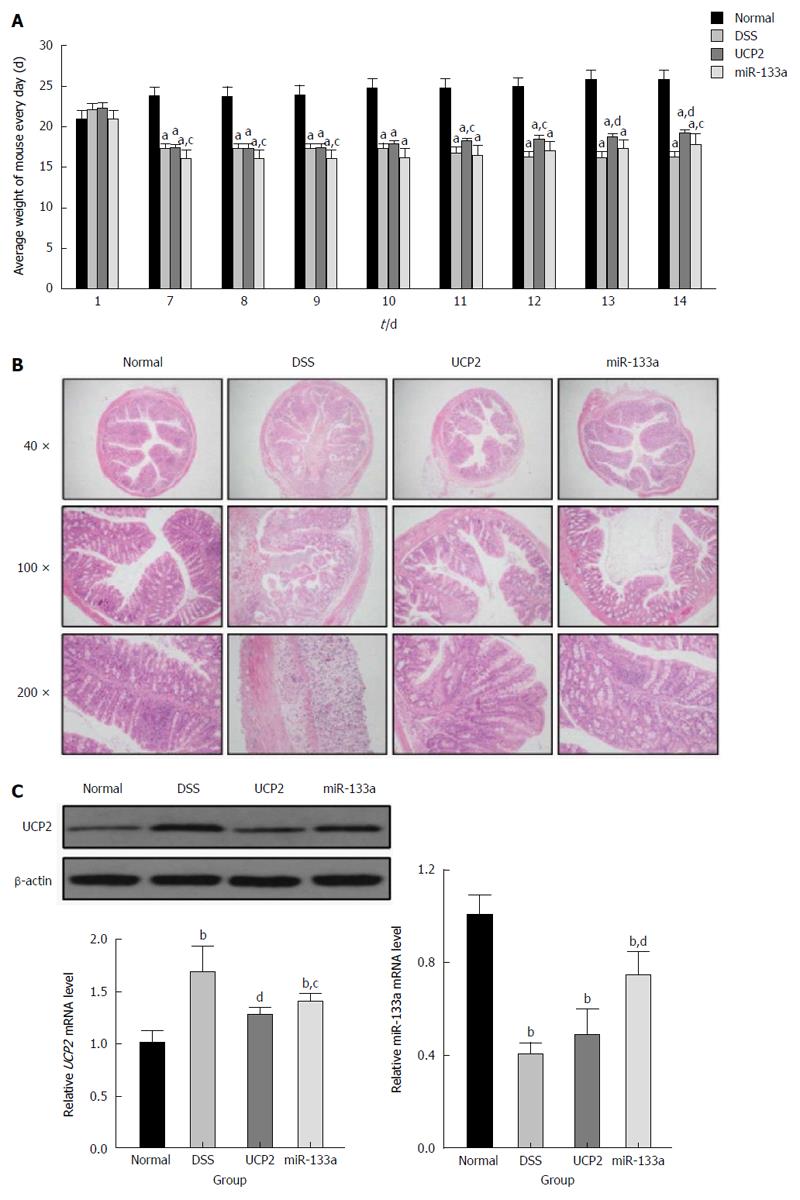
Figure 3 Inflammatory bowel disease phenotype change after the successful alteration of the UCP2 and miR-133a levels.
A: Changes in the weight of mice in the control, dextran sulfate sodium (DSS), UCP2 and miR-133a groups between days 7 and 14; B: Alleviation of IBD after the alteration of the UCP2 and miR-133a levels, as demonstrated by HE staining; C: Successful UCP2 down regulation and miR-133a up regulation in the UCP2 and miR-133a groups, as shown by Western blot and qRT-PCR, respectively. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs DSS.
- Citation: Jin X, Chen D, Zheng RH, Zhang H, Chen YP, Xiang Z. miRNA-133a-UCP2 pathway regulates inflammatory bowel disease progress by influencing inflammation, oxidative stress and energy metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(1): 76-86
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i1/76.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.76