Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2017; 23(1): 60-75
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.60
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.60
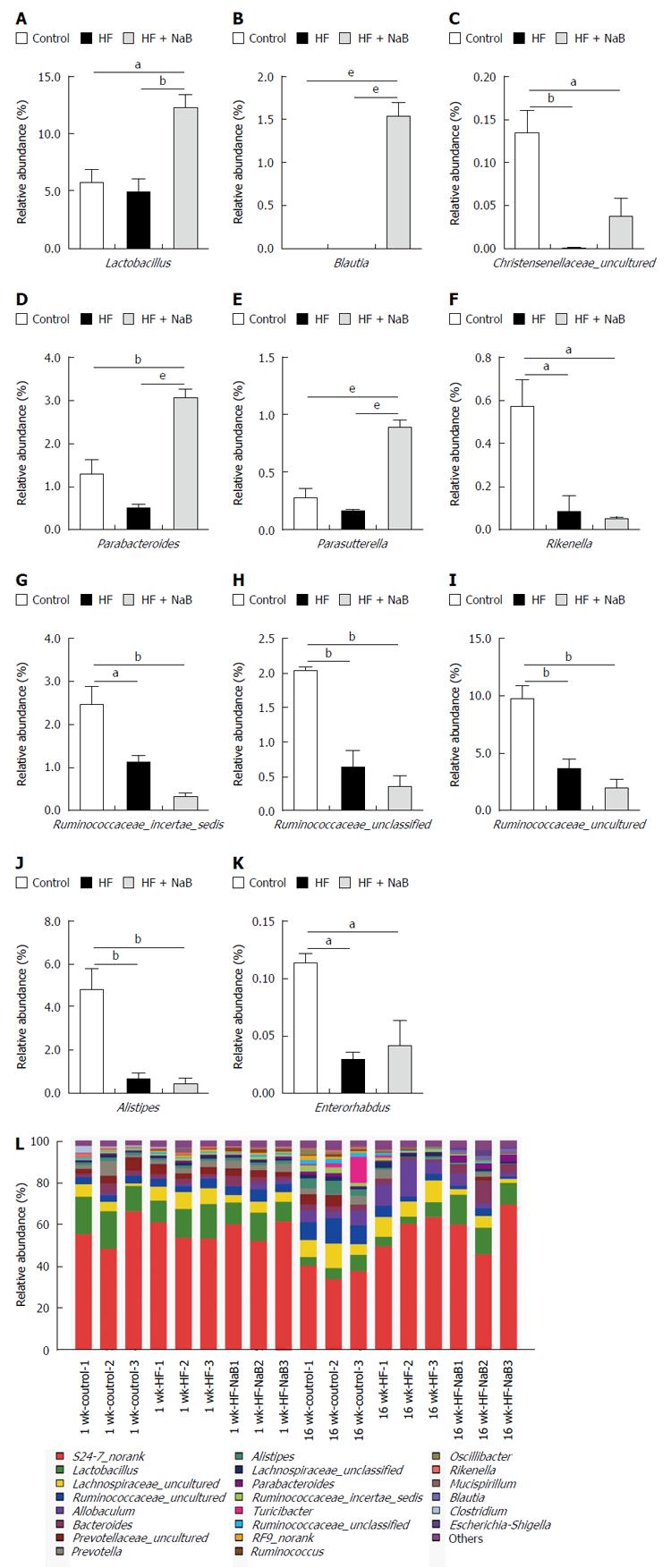
Figure 3 Influences of sodium butyrate on gut microbiota at the genus level.
A-K: Alistipes, Christensenellaceae_uncultured, Enterorhabdus, Lactobacillus, Parabacteroides, Parasutterella, Rikenella, Ruminococcaceae_incertae_sedis, Ruminococcaceae_unclassified, and Ruminococcaceae_uncultured in the HF group were lower than the control. NaB intervention reversed the changes in Christensenellaceae_uncultured, Parabacteroides, Parasutterella and Lactobacillus. NaB treatment significantly increased Blautia; L: Relative read abundance of different bacterial genera within the different communities. Sequences that could not be classified into any known group were assigned as “norank”. Data represent means ± SEM. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 and eP < 0.001.
- Citation: Zhou D, Pan Q, Xin FZ, Zhang RN, He CX, Chen GY, Liu C, Chen YW, Fan JG. Sodium butyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice by improving gut microbiota and gastrointestinal barrier. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(1): 60-75
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i1/60.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.60