Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2017; 23(1): 48-59
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.48
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.48
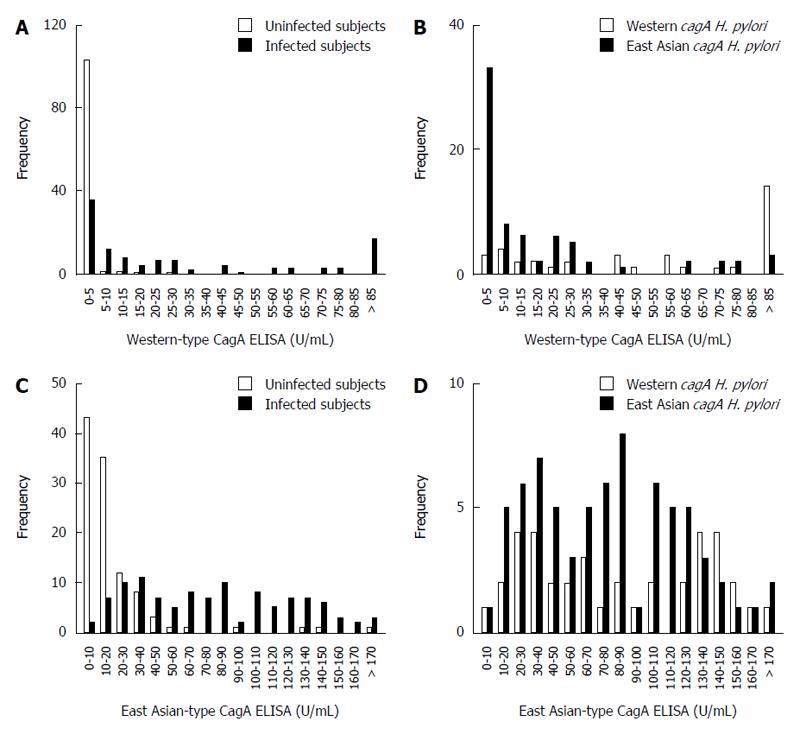
Figure 3 The distribution of CagA antibody ELISA titers is dependent on Helicobacter pylori infection status and Helicobacter pylori CagA-type.
A: Histogram of Western-type CagA ELISA titers of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-infected (gray bars) and uninfected subjects (white bars); B: Histogram of Western-type CagA ELISA titers of H. pylori infected subjects is dependent on cagA genotype; Western-type cagA H. pylori (white bars), East Asian-type cagA H. pylori (gray bars); C: Histogram of East Asian-type CagA ELISA titers of H. pylori infection and uninfected subjects. Bar coloring is the same as in (A); D: Histogram of East Asian-type CagA ELISA titers of H. pylori infected subjects is dependent on cagA genotype. Bar coloring is the same as in (B).
- Citation: Matsuo Y, Kido Y, Akada J, Shiota S, Binh TT, Trang TTH, Dung HDQ, Tung PH, Tri TD, Thuan NPM, Tam LQ, Nam BC, Khien VV, Yamaoka Y. Novel CagA ELISA exhibits enhanced sensitivity of Helicobacter pylori CagA antibody. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(1): 48-59
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i1/48.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.48