Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2016; 22(9): 2861-2866
Published online Mar 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2861
Published online Mar 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2861
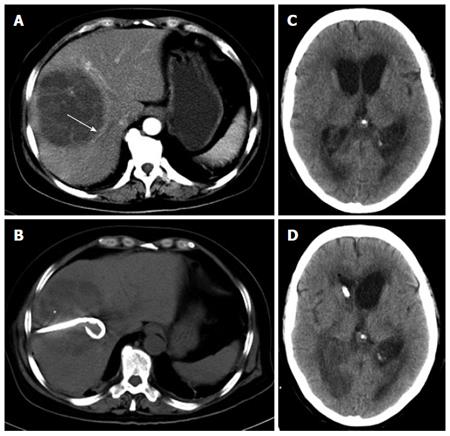
Figure 1 Computerized tomographic scan images.
A: Abdominal computerized tomographic (CT) scans demonstrated an area of abnormal attenuation measuring 84 mm × 91 mm in the right lobe of the liver, indicative of a single large multi-loculated abscess; B: Emergency CT-guided percutaneous drainage of liver abscess was performed on the night of admission; C: Enlarged lateral ventricles, low density area at the white matter near the ventricles, revealing brain edema and hydrocephalus. Brain abscesses could not be excluded; D: Emergency lateral ventricular drainage was performed when the patient’s condition deteriorated.
- Citation: Qian Y, Wong CC, Lai SC, Lin ZH, Zheng WL, Zhao H, Pan KH, Chen SJ, Si JM. Klebsiella pneumoniae invasive liver abscess syndrome with purulent meningitis and septic shock: A case from mainland China. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(9): 2861-2866
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i9/2861.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2861