Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2016; 22(8): 2545-2557
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2545
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2545
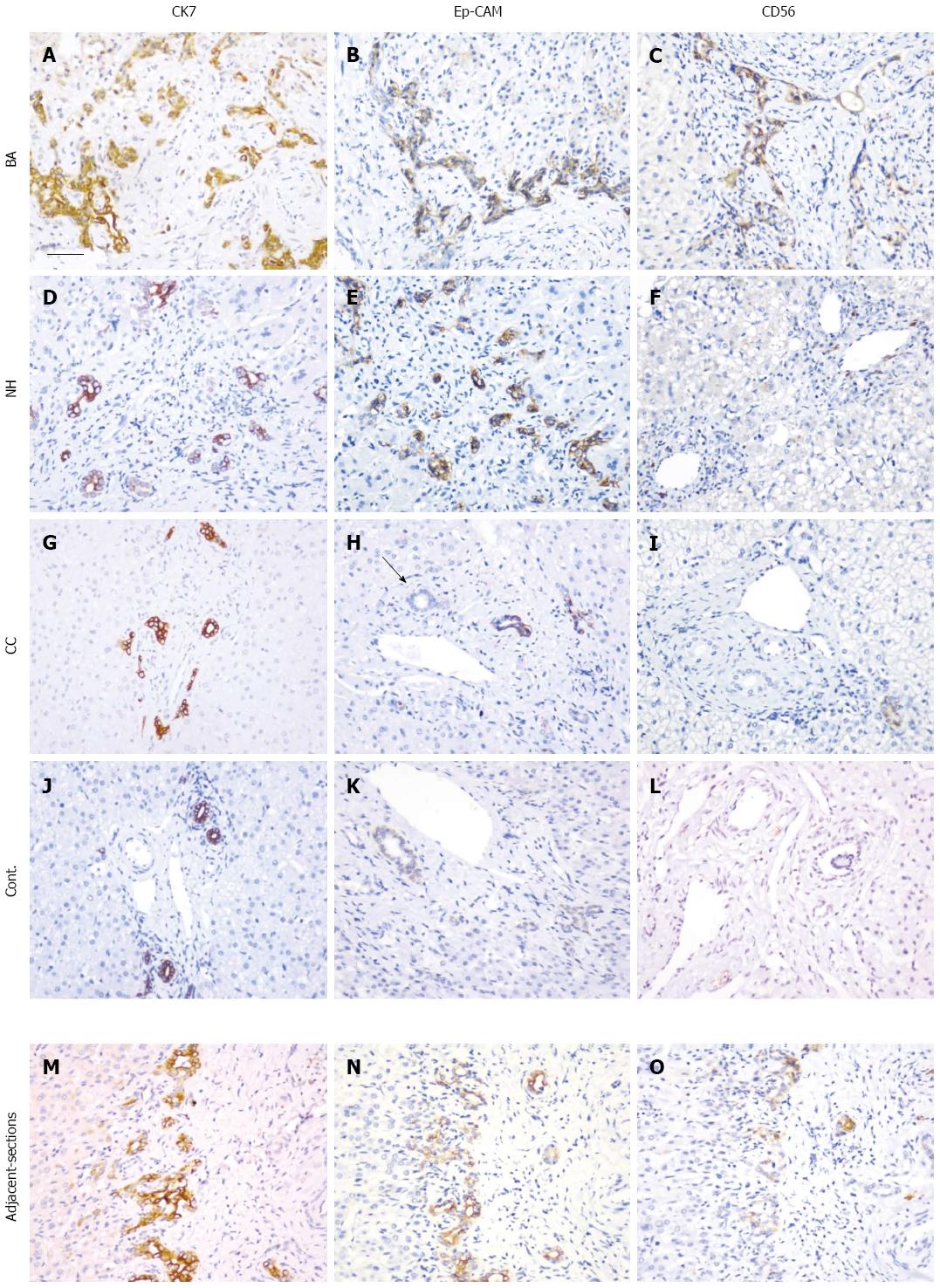
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical analysis of the expression of cytokeratin 7, epithelial cell adhesion molecule, and CD56.
Tissue sections from patients with BA (A-C), NH (D-F), CC (G-I), and the disease control (J-L) together with a set of adjacent sections (M-O) were selected. Immunohistochemical staining was performed with antibodies for CK7 (A, D, G, J and M), EpCAM (B, E, H, K and N) and CD56 (C, F, I, L and O). After antigen retrieval, the sections were incubated with antibodies overnight at 37 °C. The black arrow in (H) indicates a bile duct. The sections were examined with a Nikon light microscope. Scale bar represents 50 μm. EpCAM: Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; CK7: Cytokeratin 7; NH: Neonatal hepatitis; CC: Choledochal cyst; BA: Biliary atresia.
- Citation: Zhang RZ, Yu JK, Peng J, Wang FH, Liu HY, Lui VC, Nicholls JM, Tam PK, Lamb JR, Chen Y, Xia HM. Role of CD56-expressing immature biliary epithelial cells in biliary atresia. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(8): 2545-2557
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i8/2545.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2545