Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2016; 22(8): 2533-2544
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2533
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2533
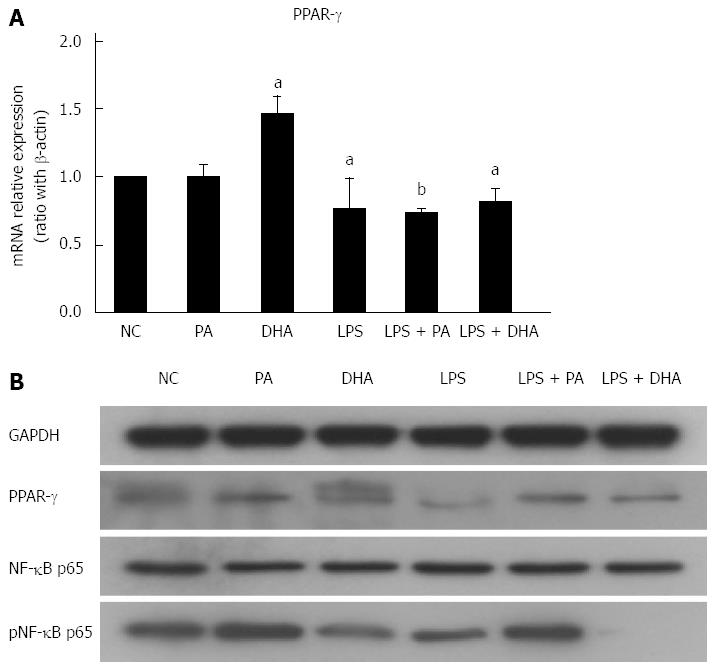
Figure 5 Effect of different fatty acids on nuclear factor-kappa B/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ expression.
Primary hepatocytes were isolated and treated with PA (0.5 mmol/L), DHA (50 μmol/L) or LPS (1 μg/mL) alone or both of them. (A) mRNA expression of PPAR-γ, (B) Protein expression of NF-κB and PPAR-γ. Values are mean ± SEM, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control, n = 3 experiments. PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; PA: Palmitic acid; DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Sui YH, Luo WJ, Xu QY, Hua J. Dietary saturated fatty acid and polyunsaturated fatty acid oppositely affect hepatic NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome through regulating nuclear factor-kappa B activation. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(8): 2533-2544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i8/2533.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2533