Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2016; 22(8): 2512-2523
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512
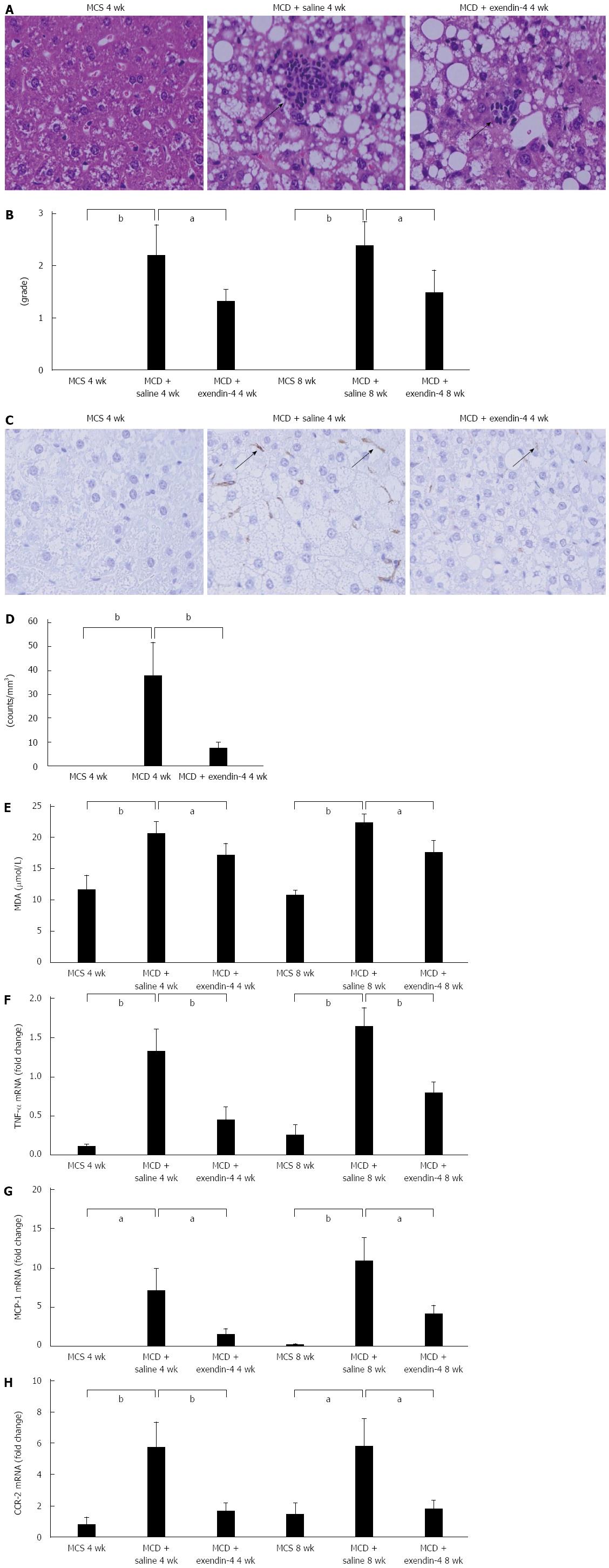
Figure 4 Evaluation of hepatic inflammation-related parameters of mice fed methionine-choline-sufficient diet, methionine-choline-deficient with exendin-4, or saline for 4 and 8 wk.
A: Representative images showing the inflammatory foci for MCD-induced liver injury at 4 wk. Original magnification, 200 ×; B: The number of inflammatory foci per 20 × field was enumerated on each section; C: Representative images of F4/80 immunoreactivity; positive cells are indicated by arrows. Original magnification, 200 ×; D: Quantitative analysis of changes in F4/80 positive cells in the respective groups; E: Evaluation of hepatic MDA levels and hepatic inflammation-related genes of mice fed MCS, MCD with exendin-4, or saline for 4 and 8 wk. Hepatic MDA levels, a marker of oxidative stress, were examined. Relative mRNA expression of TNF-α (F), MCP-1 (G), and CCR-2 (H) was evaluated in the liver. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs respective groups). MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient diet; MCS: Mice fed methionine-choline-sufficient diet ; MDA: Malondialdehyde; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1; CCR-2: cc-chemokine receptor 2.
- Citation: Yamamoto T, Nakade Y, Yamauchi T, Kobayashi Y, Ishii N, Ohashi T, Ito K, Sato K, Fukuzawa Y, Yoneda M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in non-obese mice. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(8): 2512-2523
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i8/2512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512