Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2016; 22(6): 2092-2103
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.2092
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.2092
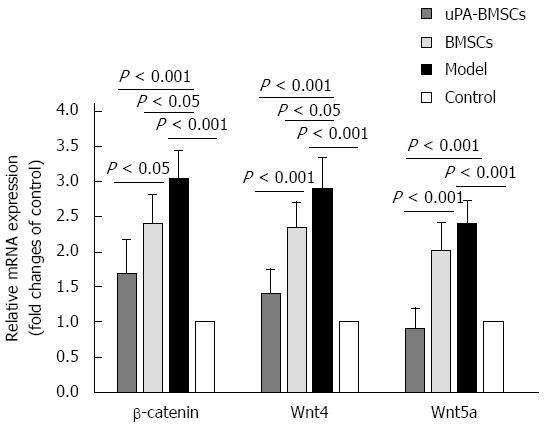
Figure 4 Effect of urokinase plasminogen activator gene modified-bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on the mRNA expression of molecules of the Wnt signaling pathway.
The bar graph shows mean relative mRNA expression levels of β-catenin, Wnt4 and Wnt5a in liver tissues. Each sample was repeated three times from each cluster. Data are normalized to GAPDH mRNA expression levels. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; BMSCs: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; uPA: Urokinase plasminogen activator.
- Citation: Ma ZG, Lv XD, Zhan LL, Chen L, Zou QY, Xiang JQ, Qin JL, Zhang WW, Zeng ZJ, Jin H, Jiang HX, Lv XP. Human urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene-modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver fibrosis in rats by down-regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(6): 2092-2103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i6/2092.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.2092