Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2016; 22(6): 1966-1974
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1966
Published online Feb 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1966
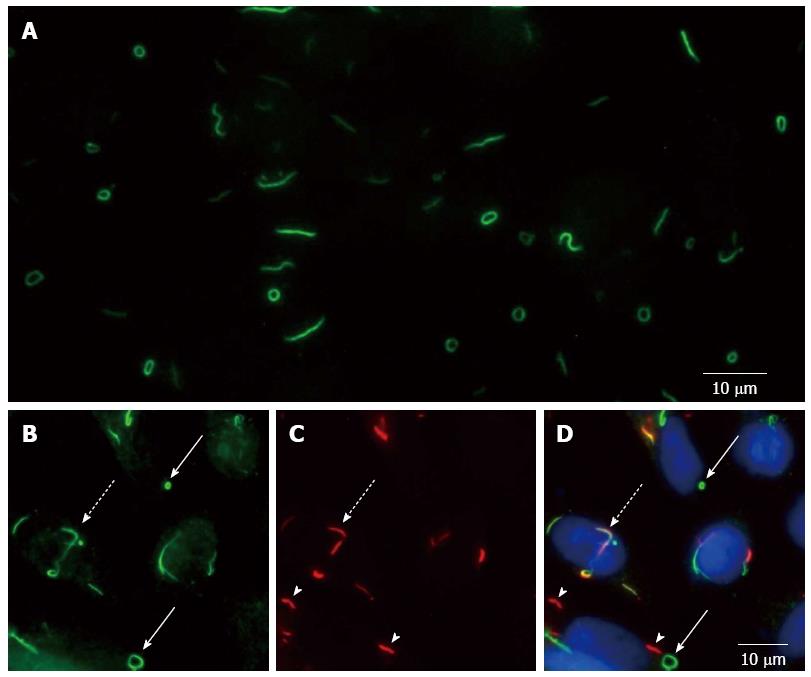
Figure 1 Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 and cytidine triphosphate synthetase enzymes can aggregate into rods and rings structures.
A: Representative image of the RR pattern observed in a Euroimmun HEp-2 slide; B-D: HEp-2 cells were cultivated with DON treatment and labeled by indirect immunofluorescence with anti-RR-positive HCV serum (B) and rabbit anti-CTPS1 antibody (C). Merged image of panel B and C plus DAPI (D). IMPDH2-based (solid arrows), CTPS-based (arrowheads), and mixed RR structures (dotted arrows) can be observed. (A-D) All data and images were obtained in our own laboratory from assays performed by Keppeke GD. RR: Rods and rings; DON: 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IMPDH2: Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2; CTPS: Cytidine triphosphate synthetase.
- Citation: Keppeke GD, Calise SJ, Chan EK, Andrade LEC. Anti-rods/rings autoantibody generation in hepatitis C patients during interferon-α/ribavirin therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(6): 1966-1974
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i6/1966.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.1966