Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2016; 22(48): 10631-10642
Published online Dec 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10631
Published online Dec 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10631
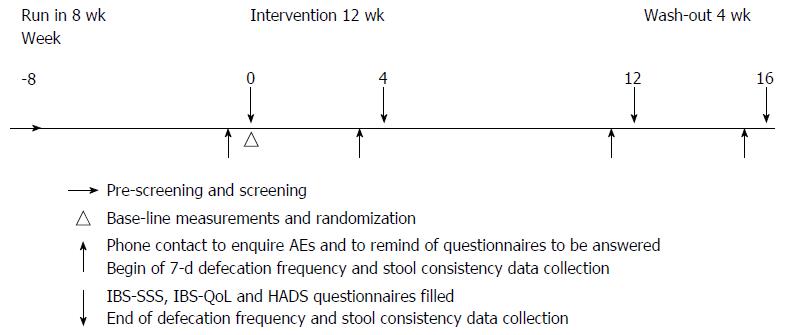
Figure 1 Study outline.
Volunteers were selected for screening visits by a prescreen for compliance over the phone. Eligible volunteers entered an 8-wk run-in period without any investigational product (IP) consumption and were thereafter randomized to receive low- or high-dose active IP or a placebo IP for 12 wk. The intervention period was followed by a 4-wk washout period without any IP consumption. Preceding each time point (weeks 0, 4, 12, and 16), volunteers recorded their stool consistency during each defecation event for 7 d. At each time point, questionnaires [Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptom Severity Score (IBS-SSS); IBS-related Quality of Life (IBS-QoL); Hospital Anxiety and Depression Score (HADS)] were filled out. All volunteers were contacted by phone prior to each sampling time point to inquire about adverse events (AEs) and to remind of the sampling procedures.
- Citation: Lyra A, Hillilä M, Huttunen T, Männikkö S, Taalikka M, Tennilä J, Tarpila A, Lahtinen S, Ouwehand AC, Veijola L. Irritable bowel syndrome symptom severity improves equally with probiotic and placebo. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(48): 10631-10642
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i48/10631.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10631