Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2016; 22(48): 10566-10574
Published online Dec 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10566
Published online Dec 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10566
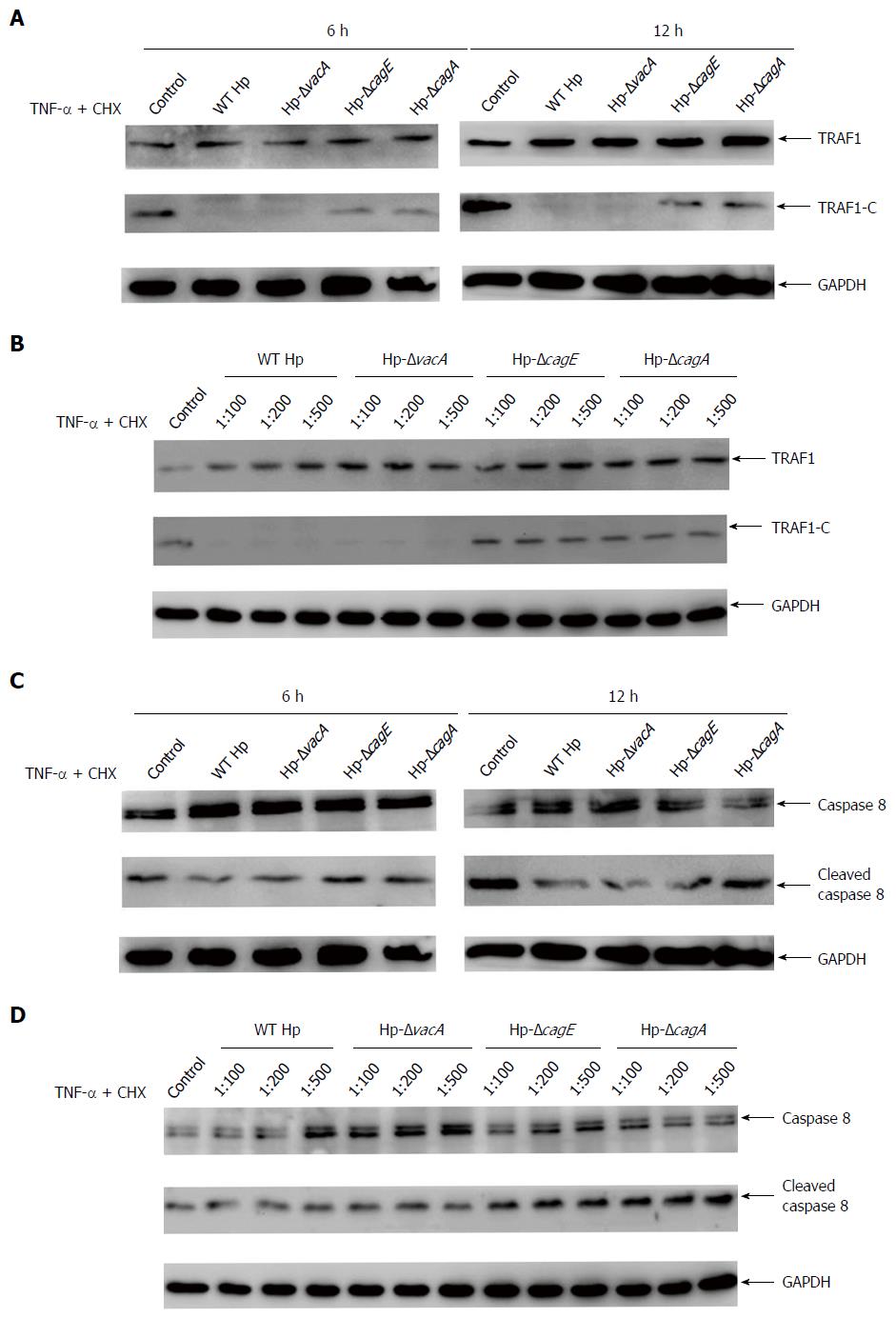
Figure 4 CagA is the major factor involved in inhibiting the cleavage of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1.
A: AGS cells transfected with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) were treated with the apoptosis inducer (0.3 μg/mL CHX and 80 ng/mL TNF-α), and co-cultured with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) strain NCTC11637 or its isogenic vacA-, cagE- or cagA-null mutants, and analyzed for the cleavage of TRAF1 at 6 h and 12 h by western blotting; B: AGS cells transfected with TRAF1 were treated with the apoptosis inducer, and co-cultured with H. pylori strain NCTC11637, or its isogenic vacA-, cagE- or cagA-null mutants at the indicated cell/bacteria ratios, and analyzed for the cleavage of TRAF1 by western blotting; C: The same as shown in (A), but analyzed for uncleaved and cleaved caspase-8 by western blotting; D: The same as shown in (B), but analyzed for uncleaved and cleaved caspase-8 by western blotting.
- Citation: Wan XK, Yuan SL, Wang YC, Tao HX, Jiang W, Guan ZY, Cao C, Liu CJ. Helicobacter pylori inhibits the cleavage of TRAF1 via a CagA-dependent mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(48): 10566-10574
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i48/10566.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10566