Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2016; 22(44): 9752-9764
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752
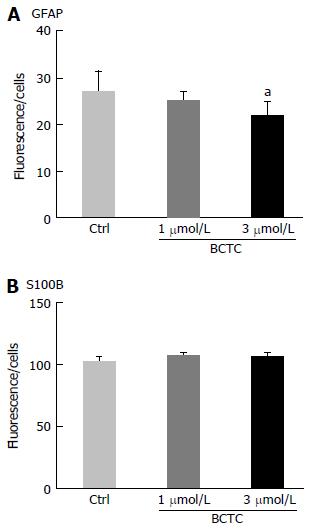
Figure 8 Effect of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 agonist/antagonist on the signal ratio of glial fibrillary acidic protein-IR to S100B-IR.
Enriched enteric glial cells [EGCs; prepared from day 5 myenteric plexus cells (MPCs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) co-culture] were plated and cultured for an additional 5 d. The TRPV1 antagonist BCTC was added and after 24 h the cells were fixed. The cells were stained with antibodies and imaging analysis was performed using a Celaview system as described in Materials and Methods. BCTC (3 μmol/L) decreased the GFAP-IR signal but the S-100B-IR signal was unchanged. Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 5-8. aP < 0.05. TRPV1: Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein.
- Citation: Yamamoto M, Nishiyama M, Iizuka S, Suzuki S, Suzuki N, Aiso S, Nakahara J. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1-immunoreactive signals in murine enteric glial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(44): 9752-9764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i44/9752.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752