Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2016; 22(44): 9752-9764
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752
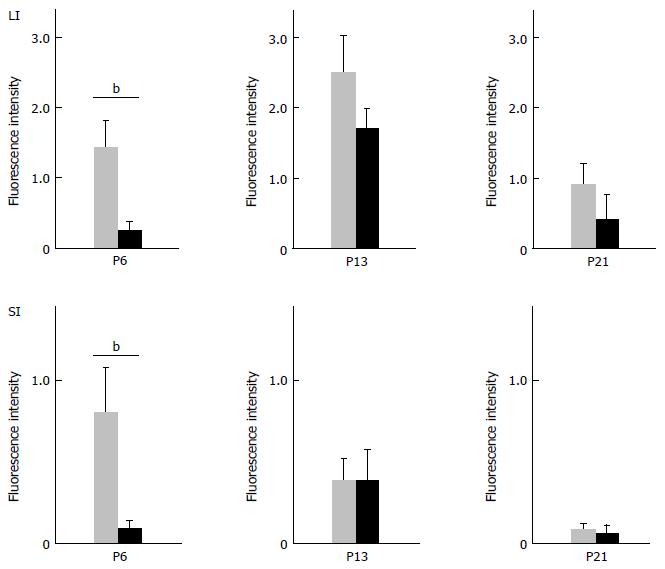
Figure 5 Difference in glial fibrillary acidic protein-IR signals between wild-type and knockout mice.
The intensity of GFAP-IR signal for WT and KO mice on postnatal day (PD) 6, PD 13 and PD 21 was quantitated by imaging analysis as described in Materials and Methods. The amount of GFAP-IR fluorescence was normalized to the circumferential length of the intestinal tract. Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 5-6. bP < 0.01. GFAP-IR: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; WT: Wild-type; KO: Knockout.
- Citation: Yamamoto M, Nishiyama M, Iizuka S, Suzuki S, Suzuki N, Aiso S, Nakahara J. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1-immunoreactive signals in murine enteric glial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(44): 9752-9764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i44/9752.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752