Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2016; 22(44): 9752-9764
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752
Published online Nov 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752
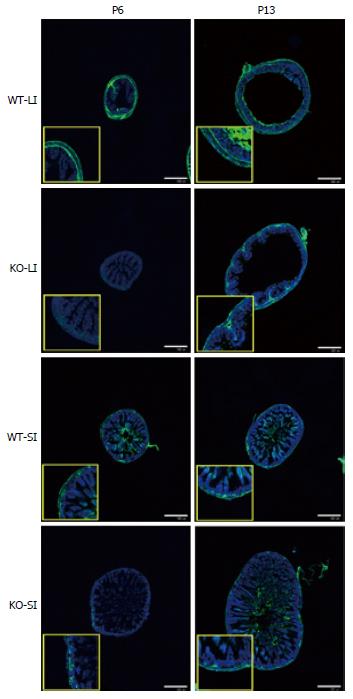
Figure 4 Difference of glial fibrillary acidic protein immunosignals between wild-type and knockout mice (image).
Large intestine (LI) and small intestine (SI) samples were isolated from WT and KO mice on postnatal day (PD) 6 and PD 13. While the GFAP-IR signal was similar in WT and KO mice on PD 13, the signal on PD 6 was weaker in KO mice than in WT mice, both in SI and LI. Nuclei were stained with TO-PRO3. Representative data of an experiment using 6 mice per each time point/group. Scale bar represents 500 μm. GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; WT: wild-type; KO: Knockout.
- Citation: Yamamoto M, Nishiyama M, Iizuka S, Suzuki S, Suzuki N, Aiso S, Nakahara J. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1-immunoreactive signals in murine enteric glial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(44): 9752-9764
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i44/9752.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9752