Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2016; 22(43): 9604-9612
Published online Nov 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i43.9604
Published online Nov 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i43.9604
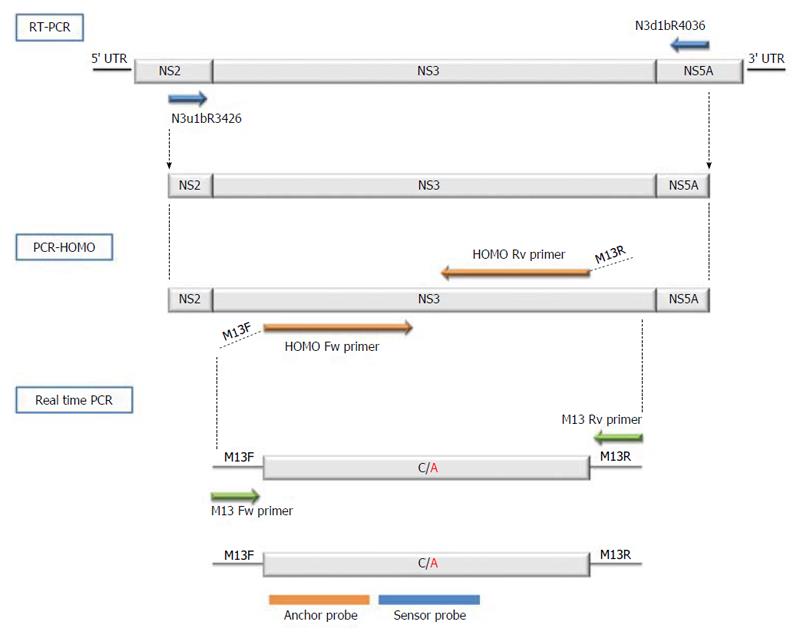
Figure 1 Diagram of the Q80K testing protocol.
RT-PCR was performed to obtain cDNA from the NS3 target containing the Q80K polymorphism, followed by HOMO-PCR performed to homogenize the Q80K flanking region using specific long primers. This PCR prepared the Q80K flanking region for the next step, in which specific probes are used to detect Q80K. The last step is a real-time PCR, in which the Q80K mutation was detected by analyzing the melting point of one of the two adjacent fluorescent-labeled probes. The specific and universal primers used are specified in each amplification step.
- Citation: Chen Q, Belmonte I, Buti M, Nieto L, Garcia-Cehic D, Gregori J, Perales C, Ordeig L, Llorens M, Soria ME, Esteban R, Esteban JI, Rodriguez-Frias F, Quer J. New real-time-PCR method to identify single point mutations in hepatitis C virus. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(43): 9604-9612
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i43/9604.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i43.9604