Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2016; 22(42): 9400-9410
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9400
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9400
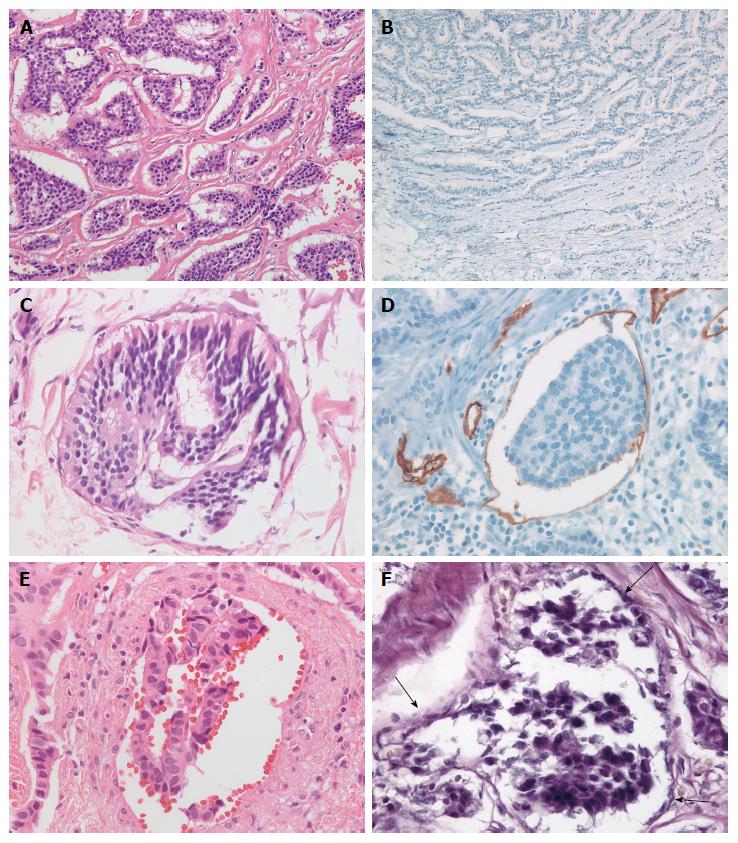
Figure 2 Ancillary staining methods.
A: Rectal neuroendocrine tumors show irregular but well-demarcated islands of uniform tumor cells separated by a fibrotic stroma; B: Negative staining for D2-40 reveals retraction cleft from the surrounding fibrotic stroma; C: Lymphatic tumor invasion with thin, endothelial cell lining on H&E is identified; D: The tumor emboli in D2-40-stained lymphatic vessels reveal the recognition of lymphatic invasion; E: Vascular invasion in H&E; F: Elastica van Gieson stain reveals vascular invasion of tumor cells (arrow).
- Citation: Kwon MJ, Kang HS, Soh JS, Lim H, Kim JH, Park CK, Park HR, Nam ES. Lymphovascular invasion in more than one-quarter of small rectal neuroendocrine tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(42): 9400-9410
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i42/9400.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9400