Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2016; 22(42): 9333-9345
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9333
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9333
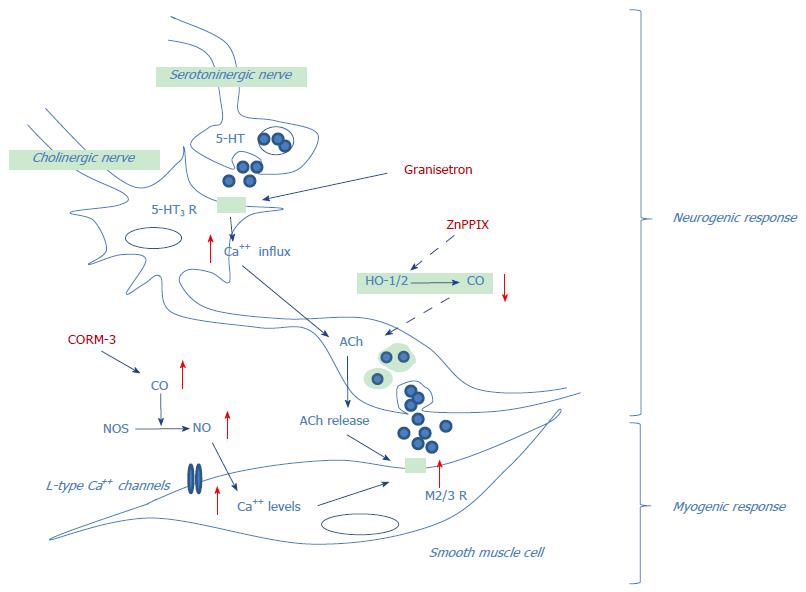
Figure 10 Potential relationship between granisetron, ZnPPIX (HO-1/2 inhibitor), and CORM-3 (CO-releasing agent) on colon neurogenic and myogenic contractile responses.
Acting on 5-HT3 receptors, granisetron may increase calcium influx, thus facilitating the release of acetylcholine (ACh) (neurogenic response), which in turn elicits a myogenic contractile response. By inhibiting the heme oxygenase (HO)-mediated carbon monoxide (CO) production, ZnPPIX may reduce the nerve terminal release of ACh, thereby counteracting granisetron effects. By releasing carbon monoxide (CO), CORM-3 may enhance the ACh-mediated myogenic contraction via a nitric oxide (NO)-dependent mechanism resulting in increased intracellular cAMP and calcium levels, with subsequent activation of L-type calcium channels and potentiation of the granisetron-mediated myogenic response.
- Citation: Nacci C, Fanelli M, Potenza MA, Leo V, Montagnani M, De Salvia MA. Carbon monoxide contributes to the constipating effects of granisetron in rat colon. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(42): 9333-9345
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i42/9333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9333