Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2016; 22(42): 9333-9345
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9333
Published online Nov 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9333
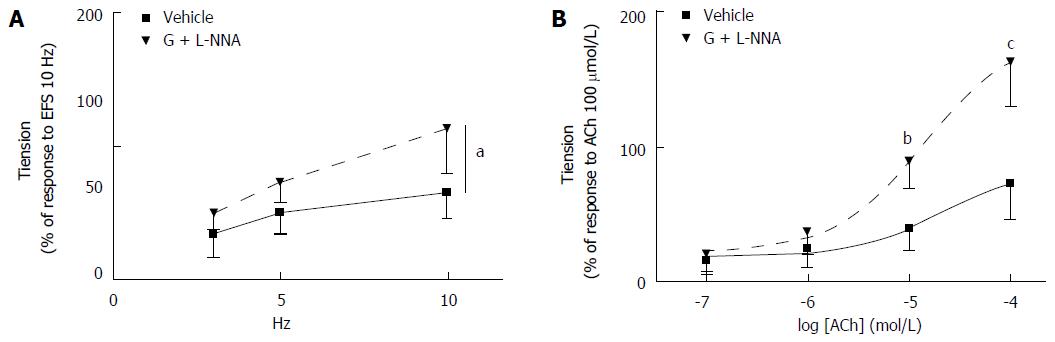
Figure 9 Effects of in vitro treatment with granisetron and NG-nitro-L-Arginine on rat colon contractile response to electrical field stimulation and to acetylcholine.
A: Co-incubation with granisetron (G) (3 μmol/L, 15 min) and NG-nitro-L-Arginine (L-NNA) (100 μmol/L, 20 min) resulted in significantly increase of electrical field stimulation (EFS)-induced contractile responses at all frequencies used compared to vehicle. ANOVA results: Ftreatments = 6.73, df = 1/11, aP = 0.025; Ffrequencies = 16.80, df = 2/22, P = 0.001; Ftreatments x frequencies = 1.26, df = 2/22, P = 0.30; B: Co-incubation with G (3 μmol/L, 15 min) and L-NNA (100 μmol/L, 20 min) resulted in significantly increased contractile response induced by acetylcholine (ACh) (10 and 100 μmol/L) compared to vehicle. ANOVA results: Ftreatments = 25.33, df = 1/11, P < 0.001; Fconcentrations = 80.22, df = 3/33, P < 0.0001; Ftreatments x concentrations = 15.8, df = 3/33, P = 0.001. T-test for ACh 10 μmol/L: t = 5.06, bP = 0.000 and for ACh 100 μmol/L: t = 4.99, cP = 0.000. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD of 6-8 experiments.
- Citation: Nacci C, Fanelli M, Potenza MA, Leo V, Montagnani M, De Salvia MA. Carbon monoxide contributes to the constipating effects of granisetron in rat colon. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(42): 9333-9345
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i42/9333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9333