Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2016; 22(41): 9117-9126
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9117
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9117
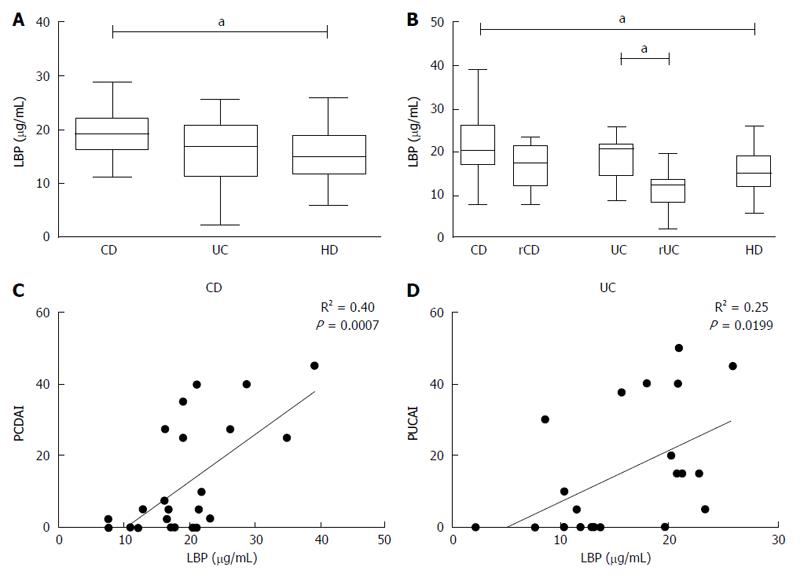
Figure 4 Dosage of LPS-binding protein and correlation with disease activity index.
A, B: Quantification of plasmatic LPS-Binding Protein (LBP) from patients affected by active Crohn’s disease (CD), remissive Crohn’s disease (rCD), active Ulcerative Colitis (UC), remissive Ulcerative Colitis (rUC) and healthy donors (HD). Data are represented with box plots using Tukey’s whiskers. Statistical significance is denoted by letters (aP < 0.05); C, D: Correlation between activity Index, expressed by PCDAI (Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Activity Index) or PUCAI (Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Activity Index) with plasmatic level of LBP in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) (C, R2 = 0.40) or Ulcerative Colitis (UC) (D, R2 = 0.25). The squared Pearson correlation coefficients (R2) and the P value are shown.
- Citation: Loganes C, Pin A, Naviglio S, Girardelli M, Bianco AM, Martelossi S, Tommasini A, Piscianz E. Altered pattern of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in peripheral blood monocytes from Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(41): 9117-9126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i41/9117.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9117