Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2016; 22(41): 9104-9116
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9104
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9104
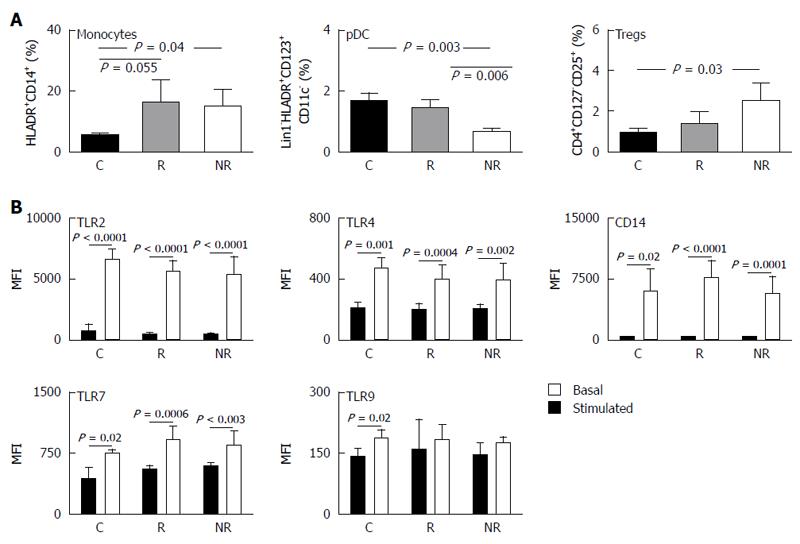
Figure 4 Peripheral blood mononuclear cells phenotype and toll-like receptor /CD14 protein levels in responders and non-responders compared to healthy controls.
A: Percentage of monocytes, pDC and CD4+ regulatory T cells were determined from total population of PBMCs isolated from responders (R, n = 12), non-responders (NR, n = 12) and healthy controls (C, n = 12) by FACS analysis. Data are expressed as mean percentage (± SD) of total cell population; B: Basal (black columns) and stimulated (white columns) TLR2, TLR4, TLR7, TLR9 and CD14 protein levels in PBMCs isolated from C (n =12), R (n =12) and NR (n = 12) were assessed by surface and intracellular staining followed by FACS analysis. Data are expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI ± SD). The P values represent statistical significance of < 0.05 between the groups as denoted. PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; TLR: Toll-like receptor; pDC: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
- Citation: Baird AC, Mallon D, Radford-Smith G, Boyer J, Piche T, Prescott SL, Lawrance IC, Tulic MK. Dysregulation of innate immunity in ulcerative colitis patients who fail anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(41): 9104-9116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i41/9104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9104