Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2016; 22(40): 8940-8948
Published online Oct 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i40.8940
Published online Oct 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i40.8940
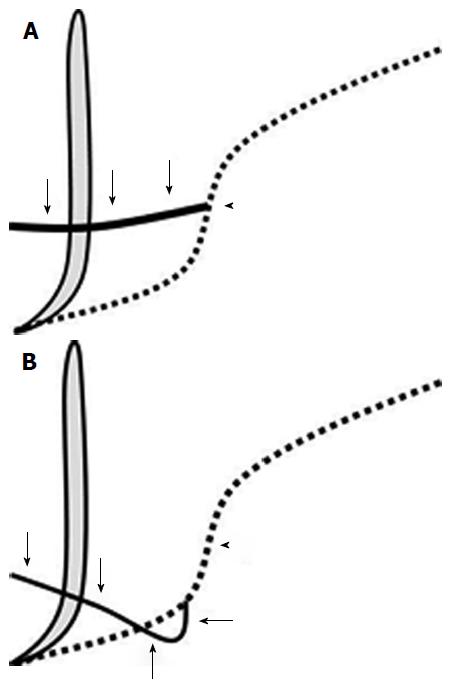
Figure 2 Schematic images of a normal pancreatic duct (A) and ansa pancreatica (B).
The vertical thick gray line indicates the common bile duct and the broken lines indicate the ventral duct. The solid black line represents the normal accessory duct in (A) and ansa pancreatica in (B). In the normal type (A), the accessory duct (arrows) arises near the flexion point (arrowhead) of the main pancreatic duct and runs towards the minor papilla horizontally and to the right. In ansa pancreatica (B), the additional duct (arrows) arises from the caudal side of the flexion point (arrowhead) of the main pancreatic duct. It runs caudally at first, then rightward and ventrally, crossing the ventral duct, and finally terminates near the minor papilla.
- Citation: Hayashi TY, Gonoi W, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi N, Ohtomo K. Ansa pancreatica as a predisposing factor for recurrent acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(40): 8940-8948
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i40/8940.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i40.8940