Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2016; 22(4): 1461-1476
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1461
Published online Jan 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1461
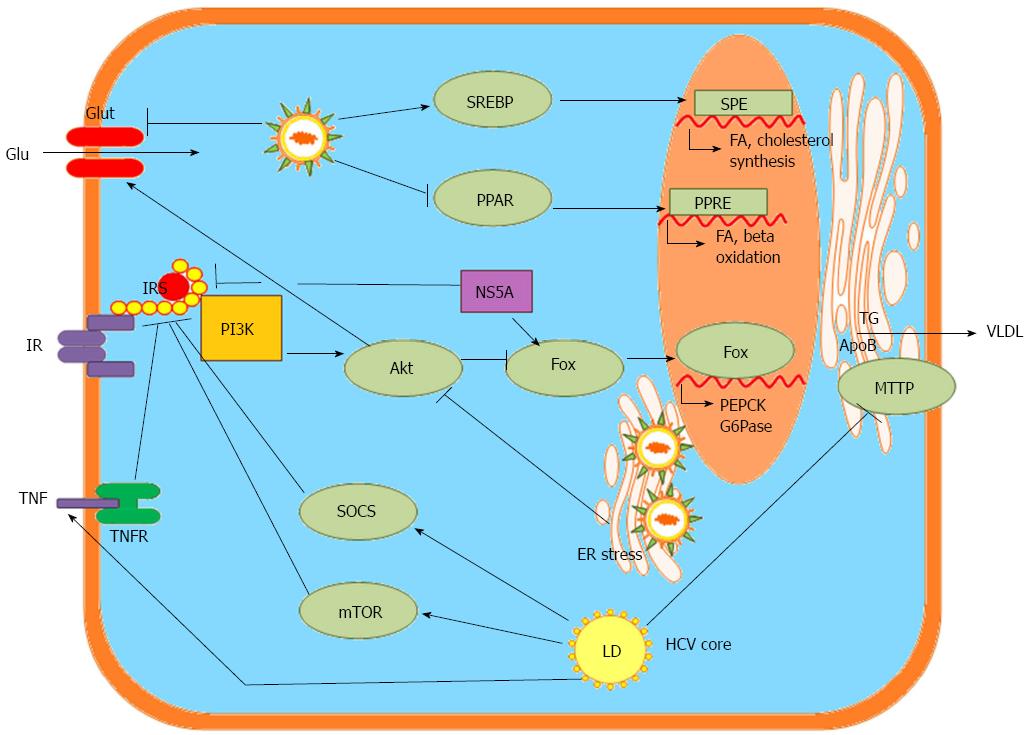
Figure 3 Hepatitis C virus-associated metabolic alterations in the hepatocyte, data from bench studies.
SREBP: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; Glu: Glucose; Glut: Glucose transporter; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; SRE: SREBP response element; FA: Fatty acid; PPRE: PPAR response element; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B: Fox: Transcription factor forkhead box; PEPCK: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; G6Pase: Glucose 6-phosphatase; IR: Insulin receptor; IRS: Insulin receptor sustrate; NS5A: HCV nonstructural protein 5 A; TG: Triglyceride; ApoB: Apoliporptoein B; MTTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; SOCS: Suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; LD: Lipid droplet.
- Citation: Chang ML. Metabolic alterations and hepatitis C: From bench to bedside. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(4): 1461-1476
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i4/1461.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1461