Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2016; 22(39): 8820-8830
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8820
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8820
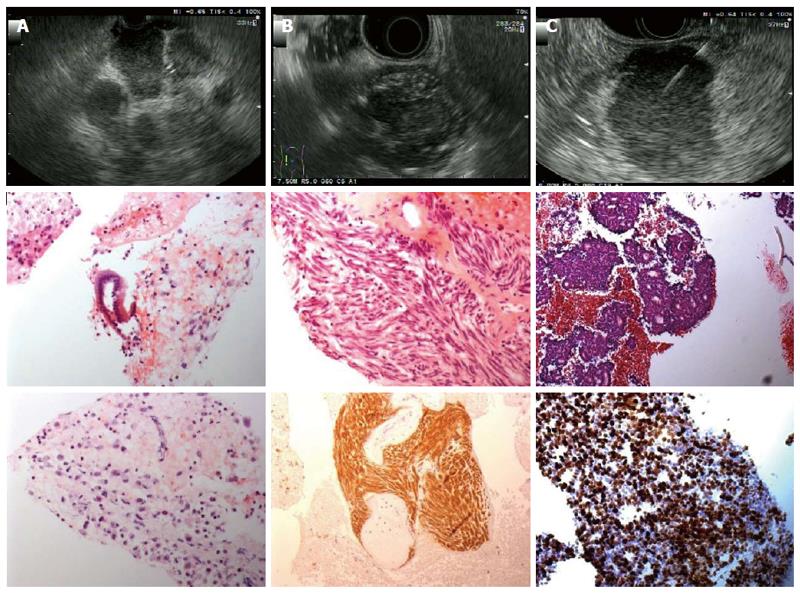
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasound and histology images from various lesions.
A: Lymph node metastases of a pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Histology shows pleomorphic carcinoma cells with anisokaryosis, high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio and prominent nucleoli [hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining]; B: Gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors originated from the muscle layer. Histology shows interlacing fascicles of uniform spindle cells with cigar-shaped nuclei (HE). Diffuse immunhistochemical positivity for CD117; C: Neuroendocrine tumors located in the pancreatic body. Histology shows sheets with rosettes of small to medium-sized, monomorphic cells with round, uniform nuclei and fine chromatin (HE staining). Immunohistochemical MIB1-proliferation rate: 80%.
- Citation: Sterlacci W, Sioulas AD, Veits L, Gönüllü P, Schachschal G, Groth S, Anders M, Kontos CK, Topalidis T, Hinsch A, Vieth M, Rösch T, Denzer UW. 22-gauge core vs 22-gauge aspiration needle for endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling of abdominal masses. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(39): 8820-8830
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i39/8820.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8820