Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2016; 22(39): 8779-8789
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8779
Published online Oct 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8779
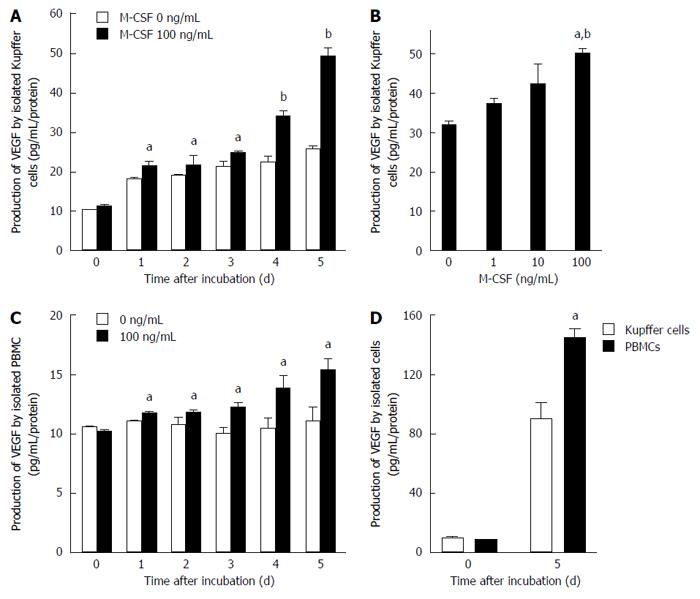
Figure 5 Production of vascular endothelial growth factor by isolated Kupffer cells and peripheral blood monocytes.
Production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by isolated Kupffer cells and peripheral blood monocytes was determined as described in the Methods. A: Kupffer cells were cultured with or without macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) in media for designated experimental periods (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs with Kupffer cells without M-CSF stimulation; and bP < 0.01 vs with Kupffer cells without M-CSF stimulation by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; B: Kupffer cells were treated with different doses of M-CSF in media, and cultured for 5 d (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs with Kupffer cells without M-CSF stimulation; and bP < 0.01 vs with Kupffer cells with 10 ng/mL of M-CSF in media by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; C: Peripheral blood monocytes were isolated and were cultured for designated experimental periods. The concentration of VEGF in media was then determined as described in the Methods (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs with peripheral blood monocytes without M-CSF stimulation by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test; D: Isolated Kupffer cells or PBMC were incubated with 100 ng/mL of M-CSF in media for 5 d. The concentration of VEGF was determined as described in Materials and Methods (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs with PBMC by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test.
- Citation: Kono H, Fujii H, Furuya S, Hara M, Hirayama K, Akazawa Y, Nakata Y, Tsuchiya M, Hosomura N, Sun C. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor expressed in non-cancer tissues provides predictive powers for recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(39): 8779-8789
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i39/8779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i39.8779