Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2016; 22(38): 8624-8630
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8624
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8624
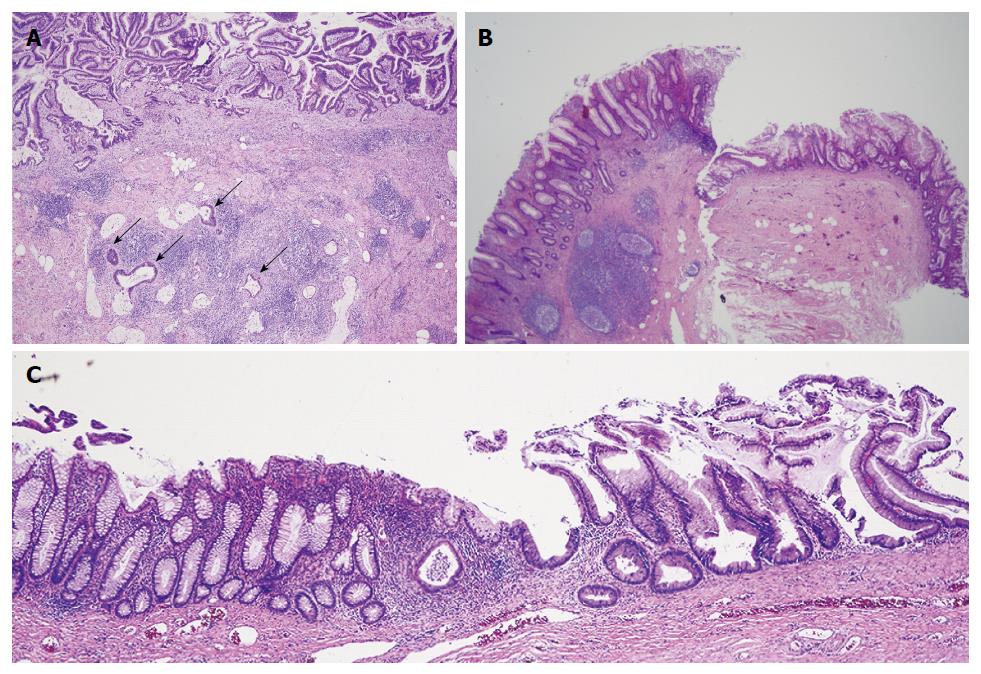
Figure 3 Microscopic pathology showed well-differentiated, invasive, mucinous, adenocarcinoma diffusely involving the appendix, sigmoid, and cecum through the serosa.
A: Low power photomicrograph of mucinous appendiceal adenocarcinoma (MAA) within fistulous (appendiceal) wall showing villoglandular adenomatous epithelium containing basophilic cells, within bizarre mucosal glands (upper area), and infiltration of cancerous mucinous glands deep in the wall (arrows). The fistulous wall also shows extensive fibrosis and chronic inflammation [hematoxylin-eosin staining (HE)]; B: Low power photomicrograph shows mucinous appendiceal adenocarcinoma with serrated glands, on the right, contiguous with normal cecal mucosa, with normal cecal glands, on the left (HE); C: Low power photomicrograph shows junction of mucinous appendiceal adenocarcinoma with serrated glands on the right, contiguous with normal sigmoid mucosa with normal glands, on the left (HE).
- Citation: Hakim S, Amin M, Cappell MS. Limited, local, extracolonic spread of mucinous appendiceal adenocarcinoma after perforation with formation of a malignant appendix-to-sigmoid fistula: Case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(38): 8624-8630
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i38/8624.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8624