Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2016; 22(38): 8519-8527
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8519
Published online Oct 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8519
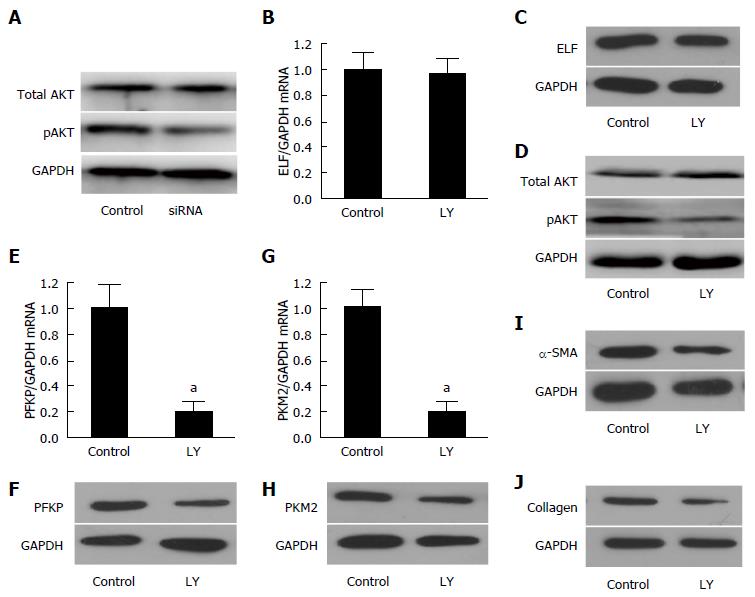
Figure 5 Embryonic liver fordin was involved in the regulation of HSC glycolysis through PI3K/AKT signaling.
A: The key protein of PI3K/akt signaling, pAKT, decreased significantly in the embryonic liver fordin (ELF)-siRNA treated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), but the expression of total AKT was not affected by ELF-siRNA treatment. GAPDH was used as the control; B, C: The Western blot and real-time RT-PCR analysis indicated that the ELF expression was not affected by Ly294002, an inhibitor of the PI3K/akt signaling; D: The pAKT expression decreased obviously after the inhibition of the PI3K/akt signaling in the HSCs; E, F: The hepatic glycolytic enzymes PFKP expression of mRNA and the protein level decreased significantly after the Ly294002 treatment in the activated HSCs (aP < 0.05 vs control); G, H: The hepatic glycolytic enzyme PKM2 expression at mRNA and the protein levels decreased significantly after the Ly294002 treatment in the activated HSCs (aP < 0.05 vs control). I, J: The main components of the extracellular matrix, α-SMA and collagen I expression showed a remarkable decrease in the activated HSCs treated by the PI3K/akt signaling inhibitor, Ly294002.
- Citation: Tu W, Ye J, Wang ZJ. Embryonic liver fordin is involved in glucose glycolysis of hepatic stellate cell by regulating PI3K/Akt signaling. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(38): 8519-8527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i38/8519.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i38.8519