Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2016; 22(37): 8334-8348
Published online Oct 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i37.8334
Published online Oct 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i37.8334
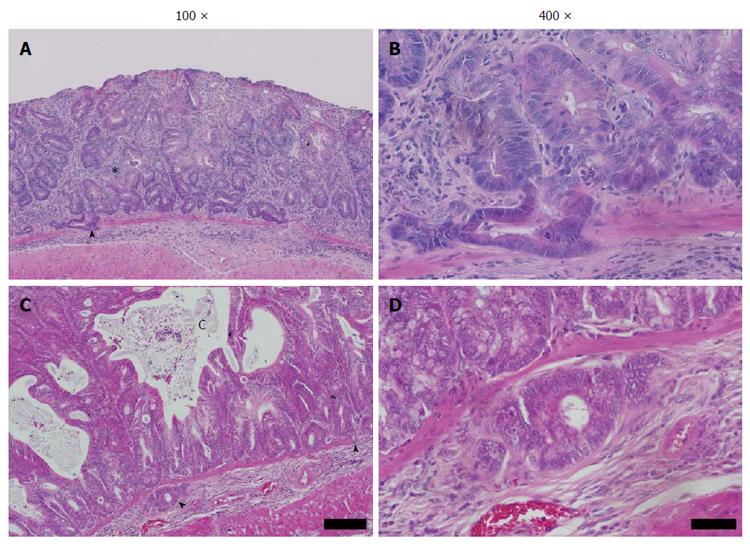
Figure 4 High-grade dysplasia and submucosal penetration in Winnie.
A: Winnie distal colonic mucosa after DSS exposure. Distorted and atypical hyperplastic glands (asterisk), with focal infiltration into underlying submucosa through an otherwise intact muscularis mucosae (arrowhead); B: Higher magnification of A. Atypical mucosal and submucosal glands display relatively bland cytology; nuclear polarity mostly intact, though nucleus: cytoplasm ratio is increased. Mitotic figures are common beyond the crypt base. Region of crypt epithelium displaying loss of nuclear polarity (arrowheads). Note the stroma surrounding submucosal glands; C: Regenerative distal colonic mucosa featuring abnormal hyperplastic crypts. Multiple large mucus-containing cysts have formed, apparently formed by confluent dilated crypts lined with hyperplastic goblet cells. Crypts displayed back-to-back arrangement associated with high-grade dysplasia; D: Higher magnification of E. Focal penetration of the submucosa by atypical mucosal crypt. Multifocal penetration of the muscularis mucosae by the overlying abnormal crypts (arrowheads). Stained with HE, scale bar represents 100 μm in A and C, 20 μm in B and D.
- Citation: Randall-Demllo S, Fernando R, Brain T, Sohal SS, Cook AL, Guven N, Kunde D, Spring K, Eri R. Characterisation of colonic dysplasia-like epithelial atypia in murine colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(37): 8334-8348
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i37/8334.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i37.8334