Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2016; 22(33): 7536-7558
Published online Sep 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7536
Published online Sep 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7536
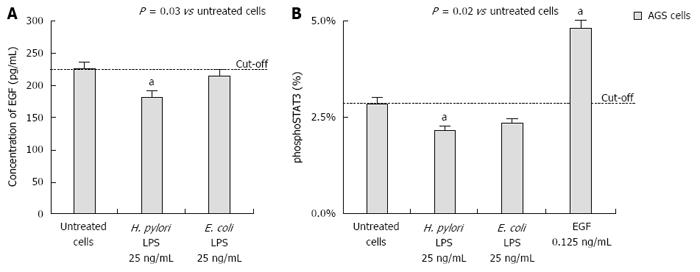
Figure 8 Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-driven inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation and epidermal growth factor production.
A: The impact of Helicobacter pylori or E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on the secretion of epidermal growth factor (EGF) by AGS cells; B: the percentage of phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (phosphoSTAT3) in AGS cells measured by cell-based ELISA. Cells treated with EGF (0.125 ng/mL) were used as a positive control. The cut-off value was related to the response of untreated cells. The data represent the average values of four independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated as aP < 0.05 vs untreated cells.
- Citation: Mnich E, Kowalewicz-Kulbat M, Sicińska P, Hinc K, Obuchowski M, Gajewski A, Moran AP, Chmiela M. Impact of Helicobacter pylori on the healing process of the gastric barrier. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(33): 7536-7558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i33/7536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7536