Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2016; 22(33): 7536-7558
Published online Sep 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7536
Published online Sep 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7536
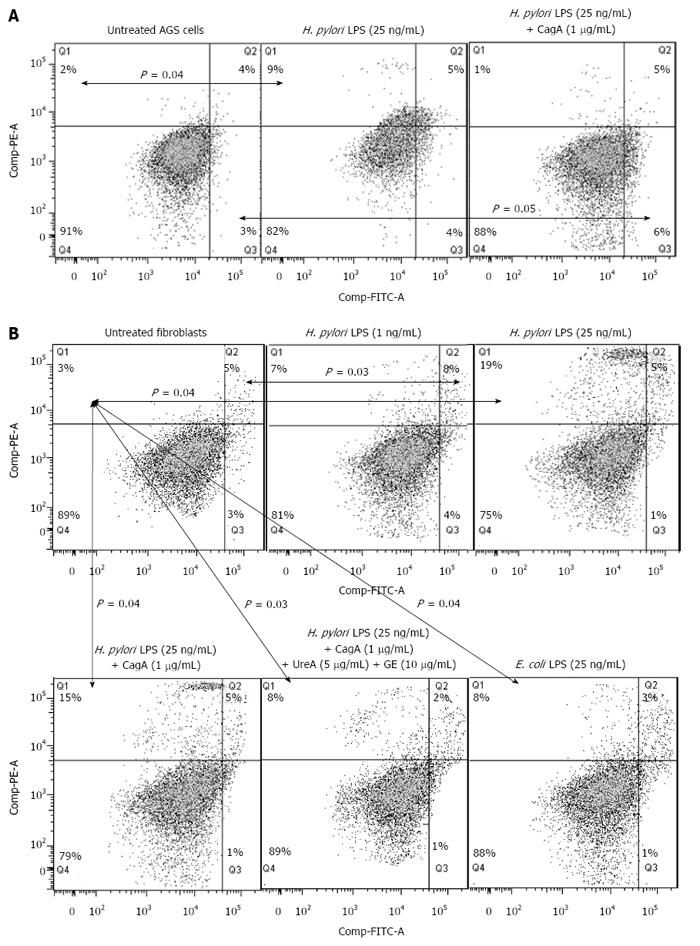
Figure 7 Type of cell death in response to Helicobacter pylori antigens.
Effects of bacterial antigens on AGS cells (A) and fibroblasts (B) concerning cell death were measured 24 h after the challenge by double staining of the cells with isothiocyanate fluorescein (FITC)-conjugated annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) using flow cytometry. Quadrants were designed as follows, Q4: Ann-V-/PI- - viable cells; Q3: Ann-V+/PI- - cells with the signs of early apoptosis; Q2: Ann-V+/PI+ - cells with the signs of late apoptosis; Q1: Ann-V-/PI+ - necrotic cells. All dot plots are a representation of equal cell populations (the fluorescence of 10000 cells was gated and counted using the FlowJo software). The data represent the average values of six independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated as P < 0.05 vs untreated cells.
- Citation: Mnich E, Kowalewicz-Kulbat M, Sicińska P, Hinc K, Obuchowski M, Gajewski A, Moran AP, Chmiela M. Impact of Helicobacter pylori on the healing process of the gastric barrier. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(33): 7536-7558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i33/7536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i33.7536