Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2016; 22(31): 7135-7145
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7135
Published online Aug 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7135
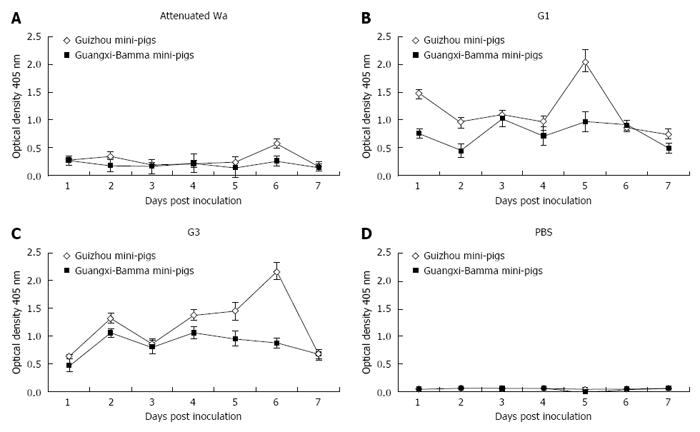
Figure 1 The curves of viral antigen-shedding in fecal samples from 3- to 5-d-old PBS or human rotavirus-inoculated mini-pigs.
The amount of viral antigen in fecal samples from the mini-pigs impregnated with 1 mL of 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human attenuated RV Wa (A), 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human RV G1 (B), 0.5 × 107 FFUs of human RV G3 (C), and 1 mL of PBS (D). Viral antigen shedding from 0 to 7 DPI was assessed by ELISA and the OD, as net readings, was identified at 450 nm. Only values exceeding 0.1 were considered positive. Fresh fecal samples from mini-pigs were collected every day and were stored at -80 °C. Every virus-inoculated group consisted of three virus-impregnated and one PBS-impregnated mini-pig to supervise transmission among mock-impregnated littermates. All the PBS inoculations were performed before any inoculation with the virus. FFUs: Focus forming units; DPI: Days post infection.
- Citation: Li JT, Wei J, Guo HX, Han JB, Ye N, He HY, Yu TT, Wu YZ. Development of a human rotavirus induced diarrhea model in Chinese mini-pigs. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(31): 7135-7145
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i31/7135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7135