Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2016; 22(3): 1034-1044
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1034
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1034
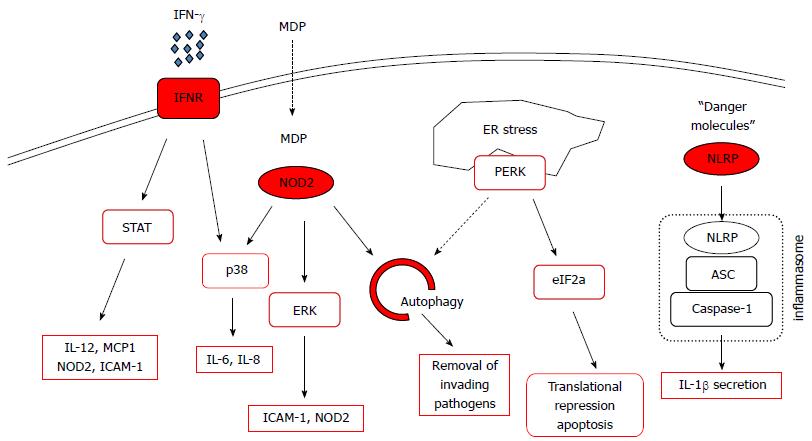
Figure 2 Signaling pathways affected by protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2.
Depicted are pathways that play important roles in intestinal homeostasis, factors with red margins are directly influenced by protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 (PTPN2). ASC: Apoptosis-associated speck containing protein; eIF2a: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A; ER: Endoplasmatic reticulum; ERK: Extracellular-stress activated kinase; ICAM-1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; MCP1: Monocyte-chemoattracting protein 1; MDP: Muramyl-dipeptide; NLRP: Nod-line receptor protein; NOD2: Nucleotide oligomerization containing 2; PERK: Protein Kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
- Citation: Spalinger MR, McCole DF, Rogler G, Scharl M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 and inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(3): 1034-1044
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i3/1034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1034