Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2016; 22(29): 6690-6705
Published online Aug 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6690
Published online Aug 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6690
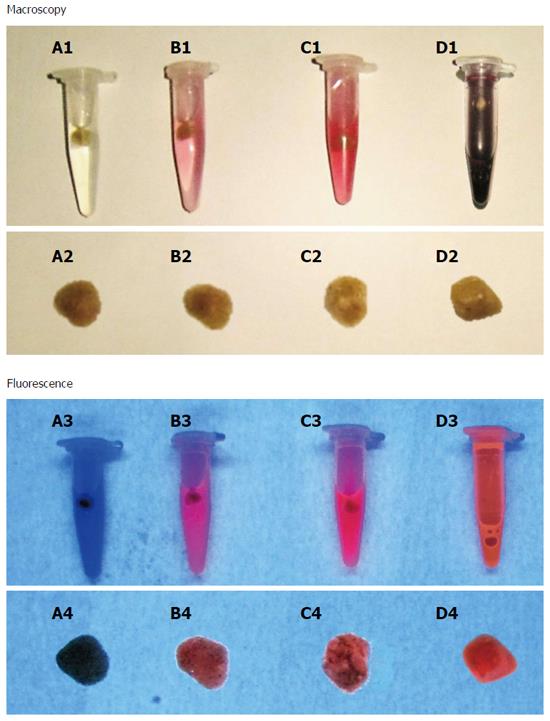
Figure 5 Macroscopic digital imaging under white and UV (365 nm) lights of human cholesterol gallstones treated with different concentrations of hypericin (2 × 10-5 - 2 × 10-3 M) or only with solvent for 72 h.
Solvent-treated stone (A1, A2) lacked fluorescence (A3, A4). Gallstones pre-incubated with hypericin solutions at 2 × 10-5 M (B1, B2), 2 × 10-4 M (C1, C2) and 2 × 10-3 M (D1, D2) exhibited fluorescence (B4, C4, D4), which seemed to increase with the hypericin concentration (B3, C3, D3).
- Citation: Miranda Cona M, Liu YW, Hubert A, Yin T, Feng YB, de Witte P, Waelkens E, Jiang YS, Zhang J, Mulier S, Xia Q, Huang G, Oyen R, Ni YC. Differential diagnosis of gallstones by using hypericin as a fluorescent optical imaging agent. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(29): 6690-6705
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i29/6690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6690