Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2016; 22(28): 6509-6519
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6509
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6509
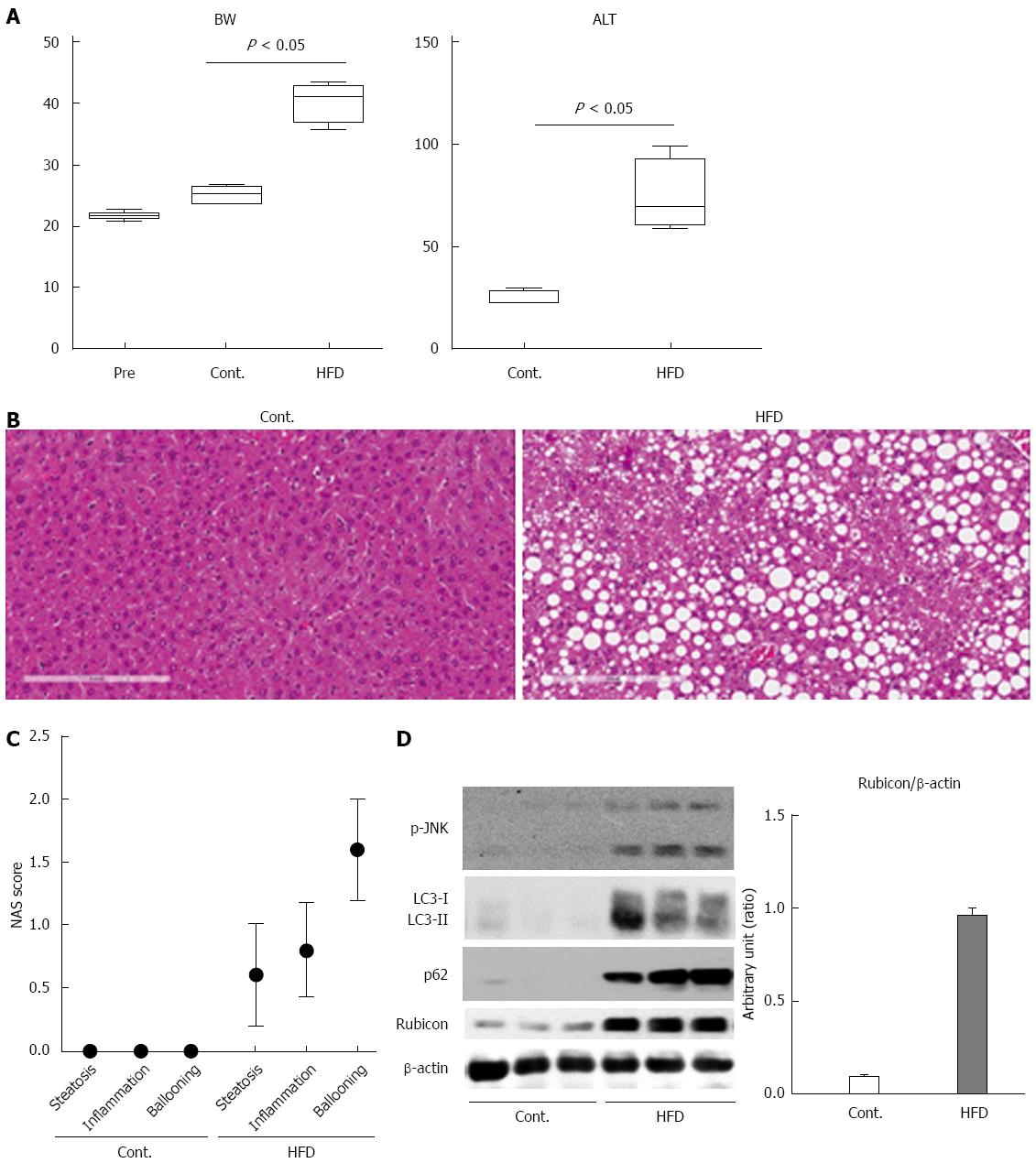
Figure 1 Mice fed high-fat diet show steatosis and inflammation of the liver, and impairment of the autophagic process.
A: The body weights of mice at the start of feeding or at 12 wk after feeding with normal chow (Cont.) or high-fat diet (HFD) are presented in the left panel. The serum ALT levels after 12 wk of feeding are shown in the right panel; B: Histology of the liver of control and HFD mice is shown in the left and the right panel, respectively (Hematoxylin and Eosin staining); C: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis activity scores (NAS) of control and HFD mice; D: Immunoblotting analyses of phosphorylated JNK, p62, LC3, Rubicon, and β-actin. Protein samples were prepared from the liver tissue of each of the control and HFD mice. All of the above experiments were repeated three times and representative results are shown. The quantitative data are presented as the means ± SD.
- Citation: Suzuki A, Kakisaka K, Suzuki Y, Wang T, Takikawa Y. c-Jun N-terminal kinase-mediated Rubicon expression enhances hepatocyte lipoapoptosis and promotes hepatocyte ballooning. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(28): 6509-6519
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i28/6509.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6509