Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2016; 22(28): 6501-6508
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6501
Published online Jul 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6501
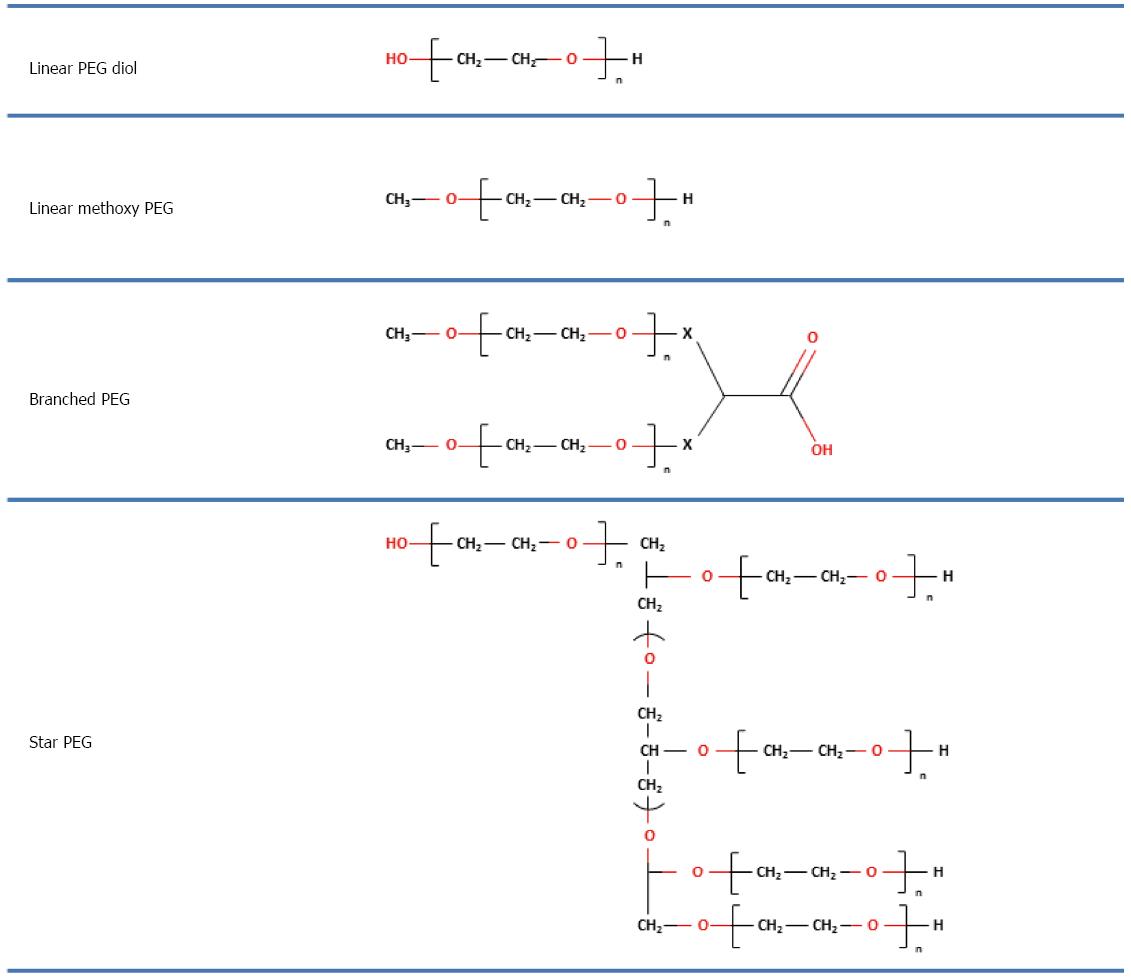
Figure 1 Schematic composition of linear, branched and star polyethylene glycols.
Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) are synthesized by a process of linking repeating units of ethylene glycol. The reaction gives products with one or two end chain hydroxyl groups termed methoxy-PEG or diol-PEG, respectively. Then, the linear PEG with branches at irregular intervals along the polymer chain forms branched PEGs. Star-shaped PEGs are the simplest class of branched PEGs with a general structure consisting of several (more than three) linear chains connected to a central core.
- Citation: Pasut G, Panisello A, Folch-Puy E, Lopez A, Castro-Benítez C, Calvo M, Carbonell T, García-Gil A, Adam R, Roselló-Catafau J. Polyethylene glycols: An effective strategy for limiting liver ischemia reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(28): 6501-6508
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i28/6501.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6501