Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2016; 22(27): 6235-6245
Published online Jul 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i27.6235
Published online Jul 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i27.6235
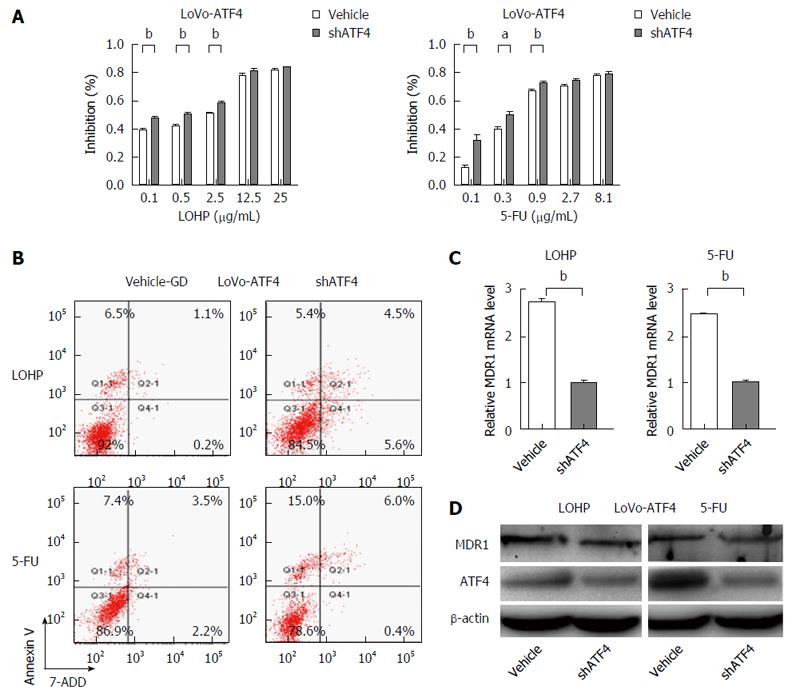
Figure 6 Inhibition of activating transcription factor 4 activity reintroduces drug sensitivity in activating transcription factor 4-overexpressing colorectal cancer cells.
A: After transfection with shATF4 or vector, ATF4-overexpressing cells were exposed to the indicated doses of LOHP or 5-FU for 48 h. Cell viabilities were determined by the CCK-8 assay; B: The apoptotic rates were much higher in the shATF4-transfected cells than in the control cells. Annexin V/7-AAD staining assay was performed to detect apoptosis; C and D: Inhibition of ATF4 decreased the MDR1 expression. The mRNA and protein levels of MDR1 in the ATF4-depleted cells were examined by qRT-PCR and Western blot, respectively, and β-actin was used as an internal controls. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vehicle vs shATF4. GD: Glucose deprivation; CRC: Colorectal cancer.
- Citation: Hu YL, Yin Y, Liu HY, Feng YY, Bian ZH, Zhou LY, Zhang JW, Fei BJ, Wang YG, Huang ZH. Glucose deprivation induces chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells by increasing ATF4 expression. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(27): 6235-6245
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i27/6235.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i27.6235