Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2016; 22(27): 6224-6234
Published online Jul 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i27.6224
Published online Jul 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i27.6224
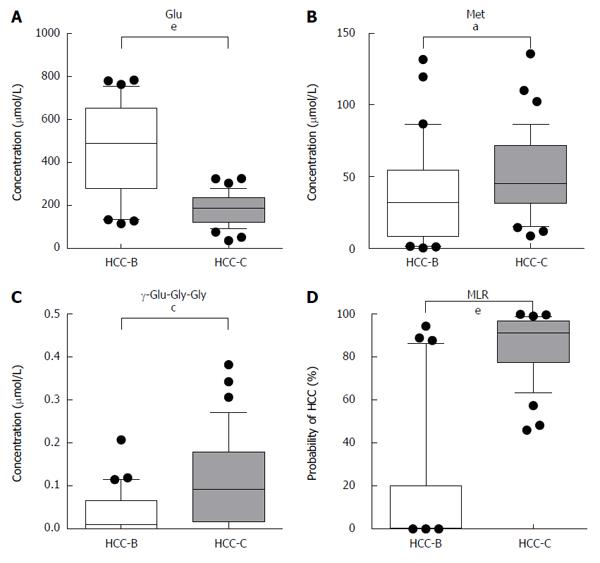
Figure 3 Serum concentrations of glutamic acid (A), methionine (B) and γ-glutamyl-glycine-glycine (C) in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
The multiple logistic regression model using these three metabolites demonstrated that they had a significant ability to discriminate between HCC-B and HCC-C (D). aP < 0.05, cP < 0.01, eP < 0.0001 between groups. Glu: Glutamic acid; Met: Methionine; γ-Glu-Gly-Gly: γ-glutamyl-glycine-glycine; MLR: Multiple logistic regression; HCC-B: Hepatitis B virus-related HCC; HCC-C: Hepatitis C virus-related HCC; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Saito T, Sugimoto M, Okumoto K, Haga H, Katsumi T, Mizuno K, Nishina T, Sato S, Igarashi K, Maki H, Tomita M, Ueno Y, Soga T. Serum metabolome profiles characterized by patients with hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis B and C. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(27): 6224-6234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i27/6224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i27.6224