Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2016; 22(25): 5822-5830
Published online Jul 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i25.5822
Published online Jul 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i25.5822
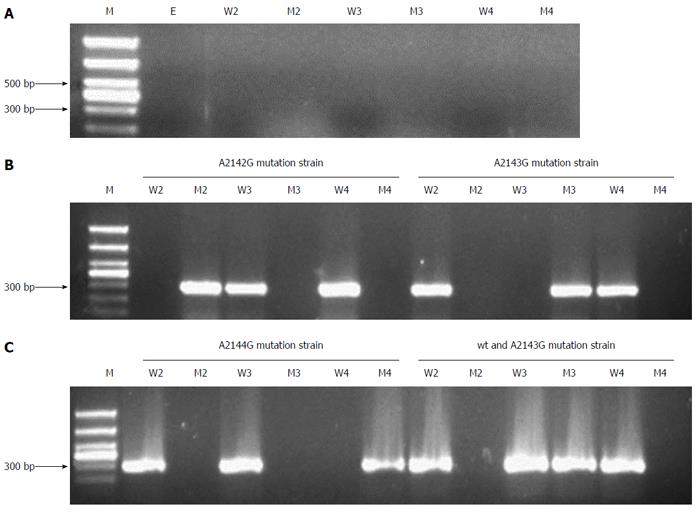
Figure 2 PCR products of Helicobacter pylori clinical strains in gastric mucosa with 2142, 2143 and 2144 positions mutation assayed by nested-ASP-PCR.
A: Helicobacter pylori-negative control; B: A2142G mutation and A2143G mutation strains; C: A2144G mutation; C: wild-type and A2143G mutation mixture strains [M: 1000 bp DNA marker (1000, 750, 500, 400, 300, 200, 100), E: Outer PCR primers, W2: 2142 wild-type primers (2142A), M2: 2142 mutation primers (2142G), W3: 2143 wild-type primers (2143A), M3: 2143 mutation primers (2143G), W4: 2144 wild-type primers (2144A), M4: 2144 mutation primers (2144G)]. ASP-PCR: Allele-specific primer-polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Luo XF, Jiao JH, Zhang WY, Pu HM, Qu BJ, Yang BY, Hou M, Ji MJ. Establishment of a nested-ASP-PCR method to determine the clarithromycin resistance of Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(25): 5822-5830
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i25/5822.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i25.5822