Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2016; 22(24): 5512-5519
Published online Jun 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i24.5512
Published online Jun 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i24.5512
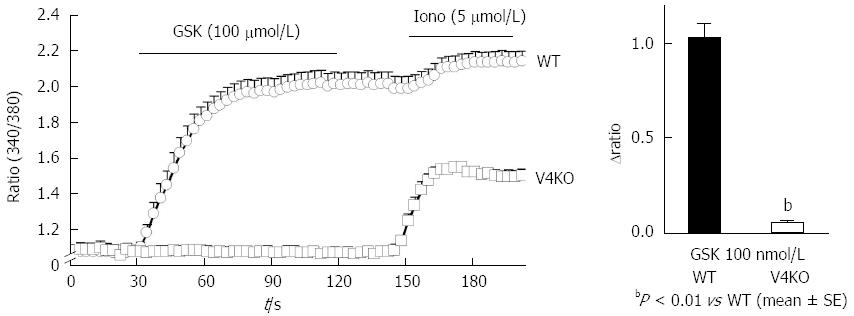
Figure 3 TRPV4-mediated increases in cytosolic Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) in mouse primary gastric epithelial cells.
A: [Ca2+]i changes (340/380 ratio) in response to the TRPV4 specific agonist GSK1016790A (GSK, 100 nmol/L) in WT or TRPV4KO (V4KO) primary gastric epithelial cells (mean ± SEM). Ionomycin (iono, 5 μmol/L) was used as a positive control. Bars indicate the period of chemical application; B: GSK significantly increased [Ca2+]i in WT cells (means ± SD; 1.03 ± 0.07, n = 20) compared to TRPV4KO cells (0.05 ± 0.01, n = 20) (bP < 0.01 vs WT).
- Citation: Mihara H, Suzuki N, Boudaka AA, Muhammad JS, Tominaga M, Tabuchi Y, Sugiyama T. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4-dependent calcium influx and ATP release in mouse and rat gastric epithelia. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(24): 5512-5519
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i24/5512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i24.5512