Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2016; 22(23): 5353-5363
Published online Jun 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5353
Published online Jun 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5353
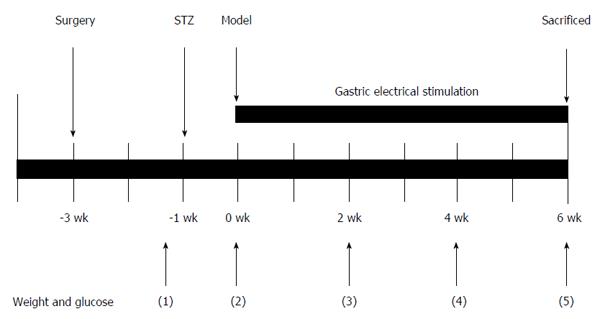
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the gastric electrical stimulation study protocol.
After surgery of electrode implantation, the rats had 2 wk to recover from the surgery. After streptozotocin injection, the diabetic rats were randomized into four large groups depending on the parameter of gastric electrical stimulation (GES): DM (diabetic group) + SGES (diabetic with sham GES), DM + GES1 (GES parameter 1), DM + GES2 and DM + GES3 groups for 6 wk. GES was adopted for 30 min/d, 7 d/wk during the whole process of the experiment. The body weights and blood glucose levels were measured before the injection of STZ and during weeks 0, 2, 4, and 6 after the induction of diabetes.
- Citation: Li H, Chen Y, Liu S, Hou XH. Long-pulse gastric electrical stimulation protects interstitial cells of Cajal in diabetic rats via IGF-1 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(23): 5353-5363
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i23/5353.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5353