Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2016; 22(22): 5211-5227
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5211
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5211
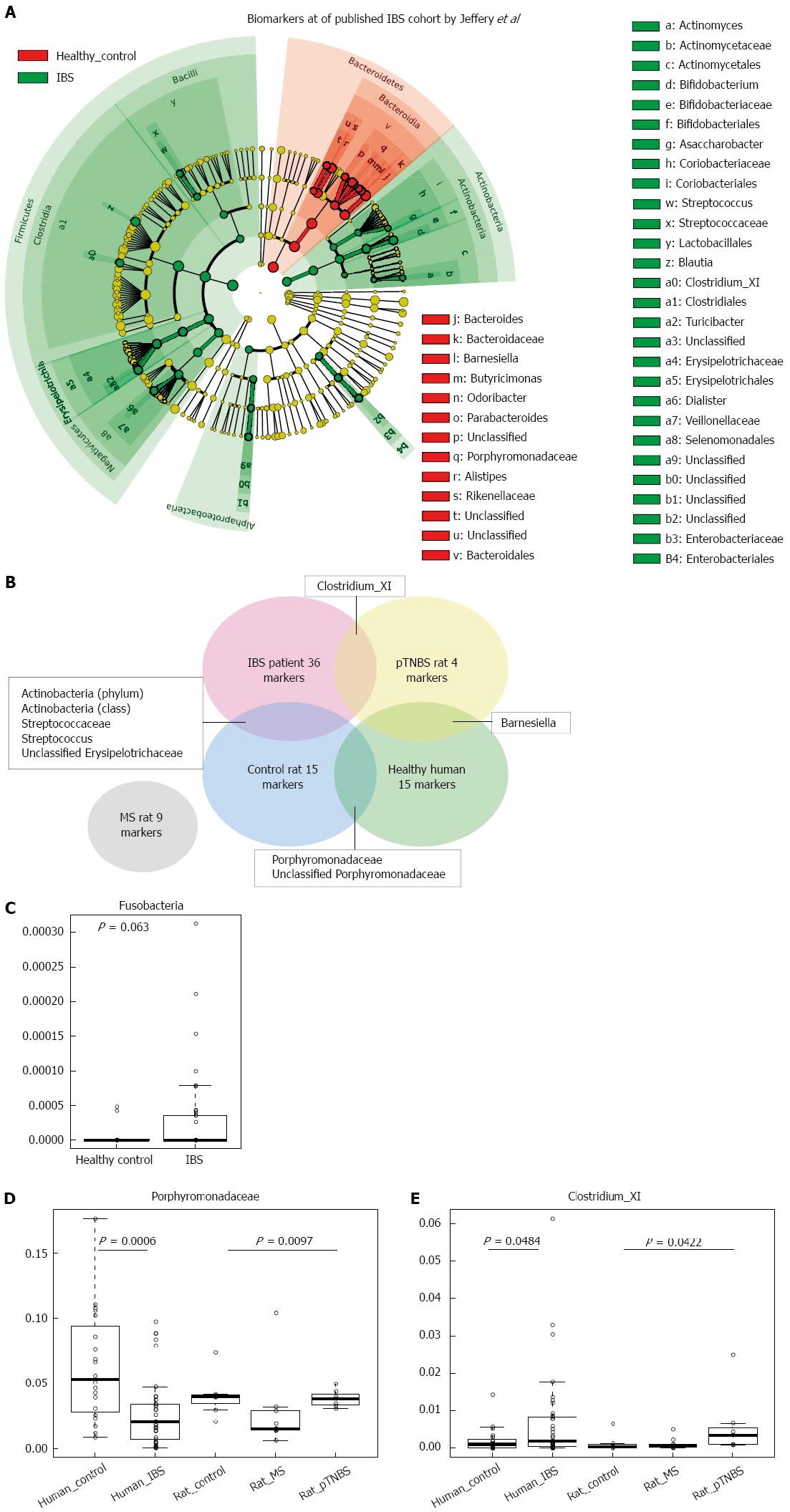
Figure 6 Comparing rat model dysbiosis to that of Jeffery’s human irritable bowel syndrome cohort.
A: Cladogram indicates the biomarkers of different abundances between groups; B: Venn plot of the positive (increased) biomarkers shared by rat models and Jeffery’s human IBS cohort. The overlapped area indicates that the two groups have common biomarkers. The MS rat does not share biomarkers from the human cohort; C: Abundance of the Fusobacteria phylum marginally increased in the human IBS cohort; D: Abundance of Porphyromonadaceae in fecal samples of healthy human controls, human IBS patients, control rats, MS rats, and pTNBS rats. Porphyromonadaceae was depleted in both the human IBS group and the MS rats; E: Abundance of Clostridium XI in fecal samples of healthy human controls, healthy IBS patients, control rats, MS rats, and pTNBS rats. Clostridium XI increased in both human IBS patients and pTNBS rats. IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; MS: Maternal separation; pTNBS: TNBS post-inflammatory.
- Citation: Zhou XY, Li M, Li X, Long X, Zuo XL, Hou XH, Cong YZ, Li YQ. Visceral hypersensitive rats share common dysbiosis features with irritable bowel syndrome patients. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(22): 5211-5227
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i22/5211.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5211