Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2016; 22(22): 5183-5192
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183
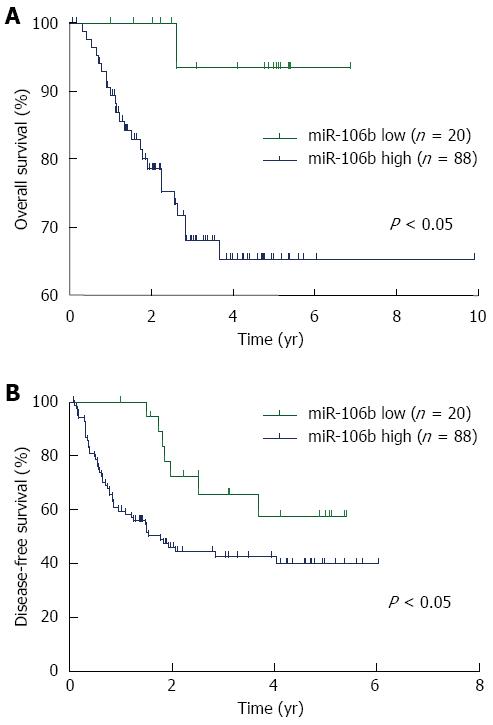
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier overall and disease-free survival curve of patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma based on miR-106b expression (n = 108).
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients were divided into two groups including miR-106b low (n = 20) and miR-106b high (n = 88) groups based on the expression levels of miR-106b. A: Overall survival curve; B: Disease-free survival curve. Log-rank test was used for statistical analysis. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
- Citation: Yen CS, Su ZR, Lee YP, Liu IT, Yen CJ. miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(22): 5183-5192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i22/5183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183