Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2016; 22(22): 5183-5192
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183
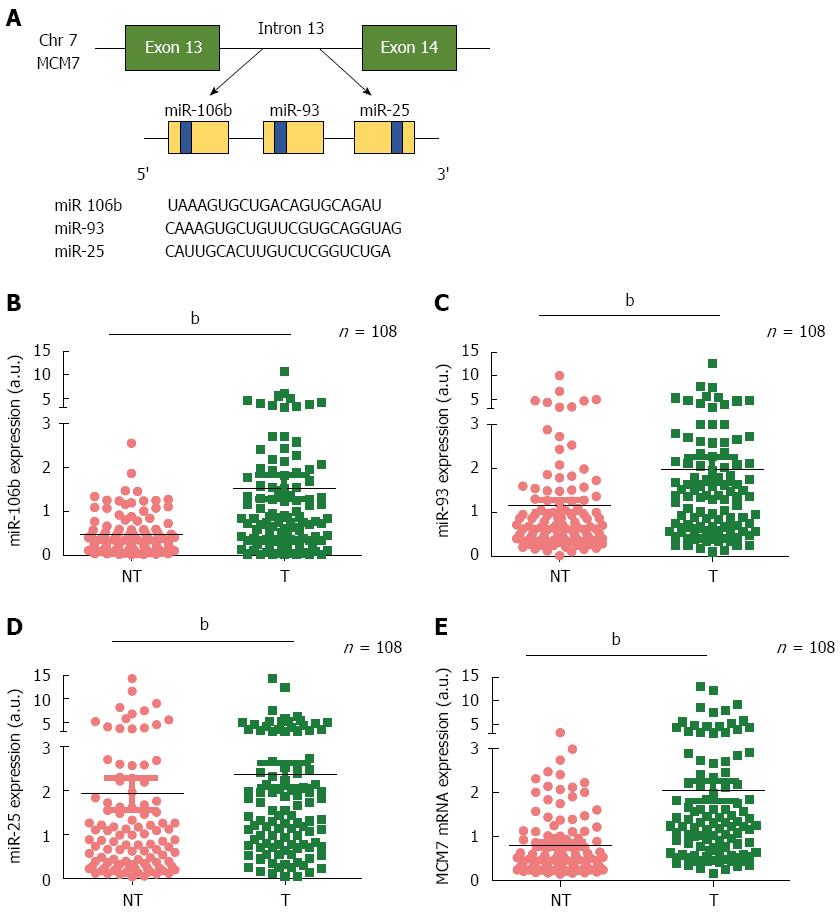
Figure 2 The mRNA expression levels of the miR-106b-25 cluster and MCM7 in tumor and non-tumor regions of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients (n = 108).
A: Schematic representation of the miR-106b-25 cluster of miRNA (miR-106b, miR-93 and miR-25) within the 13th intron of the MCM7 gene. The yellow boxes represent pre-miRNAs. The blue boxes represent mature miRNAs; B-E: miR-106b (B), miR-93 (C), miR-25 (D), and MCM7 (E) expression levels in the tumor and non-tumor regions of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, determined using q-RT-PCR. bP < 0.001 NT vs T. a.u.: Arbitrary unit.
- Citation: Yen CS, Su ZR, Lee YP, Liu IT, Yen CJ. miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(22): 5183-5192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i22/5183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183